아토피 피부염의 한약 치료에 대한 무작위대조군연구 중심의 연구 동향 - CNKI를 중심으로
Ⓒ The Society of Pathology in Korean Medicine, The Physiological Society of Korean Medicine
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to analyze the research trends of randomized controlled trials on herbal medicine treatment for atopic dermatitis in China for the last 5 years. We searched for randomized controlled trials with the intervention of herbal medicine for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in the CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure) from January 2014 to December 2018. For the screening of the paper, we used ‘特应性皮炎’ and ‘异位性皮炎’ which mean atopic dermatitis and search was limited to three areas within Medicine & Public Health: Traditional Chinese Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herbs, Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine with Western Medicine. Among the 136 searched studies, we selected a total of 34 studies and analyzed a year of publication, subject characteristics, study design and intervention, prescribed herbal medicine and herbs, pattern identification, evaluation criteria, and outcomes. Longmu decoction (龍牡湯) and Polia Sclerotium (茯笭) was the most frequently prescribed medicine and herb. The most commonly used pattern identification was Blood deficiency and Wind-dryness (血虛風燥), and among them, the most frequently prescribed herb is Rehmanniae Radix (生地黃). In most studies using the total effectiveness and SCORAD index as an outcome measure, the herbal medicine treatment group showed statistically better results than the control group. As a result of the safety assessment, the herbal medicine treatment group was reported having significantly fewer side effects compared to the control group. Hence, it was confirmed that the intervention including herbal medicine had a significant effect on atopic dermatitis. This study would be able to provide the basis of clinical research on atopic dermatitis and applied to the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Keywords:
Atopic Dermatitis, CNKI, Herbal Medicine, Randomized Controlled Trial, Research Trends서 론
아토피 피부염(Atopic dermatitis)은 가려움과 피부 건조 및 특징적인 습진성 병변을 동반하며 악화와 호전을 반복하는 만성 염증성 피부질환이다1). 증상은 주로 영유아기에 시작되어 전 연령에 걸쳐 나타나며, 중등도 이상의 아토피 피부염을 보이는 경우의 30%에서는 증상이 성인기까지 지속되어 사회생활에 많은 지장을 받는다2). 국내외적으로 아토피 피부염의 유병률은 증가 추세를 보이며3) 중증 환자의 비율도 점차 증가하고 있다4).
현재까지 아토피 피부염은 정확한 원인 및 발병 기전이 명확하게 밝혀져 있지는 않으나 유전적, 환경적, 심리적, 면역학적 인자 및 피부 장벽 기능 이상 등이 복합적으로 관여하는 것으로 추정된다5). 아토피 피부염의 서양의학적 치료로는 국소 및 전신 스테로이드제, 항히스타민제, 면역억제제, 광선치료, 생물학적 제제 등이 있다6). 하지만 이러한 기존의 치료법들은 일시적으로 증상을 완화시킬 수는 있으나 근본적인 치료는 어려운 실정이다. 더욱이 가장 기본적으로 선택되는 치료제인 스테로이드제의 장기적 사용은 표피 및 진피조직의 위축과 약화로 인한 모세혈관 확장, 골밀도 감소, 고혈압, 소아의 성장 억제 등의 부작용을 일으키기도 하며, 일부 환자의 경우 치료제에 대한 내성으로 인하여 더 이상 반응하지 않고 증상이 더욱 악화되기도 한다7).
아토피 피부염은 한의학적으로 奶癬, 四彎風, 胎㾾瘡, 血風瘡, 濕瘡, 浸淫瘡 등의 범주에 해당한다. 증상에 따라 風熱, 血熱, 濕熱溫燥, 脾胃濕熱, 血虛風燥 등의 변증으로 분류하여 치료하며 한약을 비롯한 한방 외용제, 침구 요법 등 다양한 치료법이 활용되고 있다8). 서양의학적 치료의 한계로 인하여 아토피 피부염의 한의학적 치료가 임상에서 활발히 이루어지고 있으나 한의학을 적용한 아토피 피부염 연구 중 근거 수준이 높은 무작위 대조군 임상 연구는 다른 질환에 비하여 부족한 실정이다9). 또한 박 등10)이 국내에서 시행된 아토피 피부염을 대상으로 한 무작위 대조군 연구에 관하여 분석한 결과 대다수가 한방 외용제를 중재로 한 연구였음을 보고하였다.
이에 저자는 아토피 피부염에 대하여 한약을 이용한 임상적 치료의 근거자료가 필요하다고 판단하여 2014년부터 2018년까지 최근 5년간 중국에서 발표된 아토피 피부염의 한약 치료에 대한 무작위 대조군 연구 결과를 토대로 임상 연구 동향을 고찰하였다. 특히 본 연구는 아토피 피부염에 사용된 한약 치료의 변증 및 사용된 본초를 중점적으로 분석하였으며 이를 통하여 아토피 피부염의 한의학적 치료와 임상 연구의 기초 자료를 마련하고자 하였다.
연구대상 및 방법
1. 연구 대상
최근 5년간 중국에서 시행된 무작위 대조군 임상 연구 (randomized controlled clinical trial, RCT)로서 아토피 피부염 환자를 대상으로 경구 한약 치료를 중재 시술(intervention treatment)로 한 연구를 선정 기준으로 정하였다. 제외 기준은 원저가 아닌 연구(고찰 및 리뷰 논문), 원문이 존재하지 않는 연구, 중복으로 출판된 연구, 동물을 대상으로 한 연구, 환자-대조군 연구, 증례군 및 증례 연구, 침구 치료를 중재로 한 연구, 치료군이 한약을 경구 복용하지 않은 연구, 대조군에 경구 한약 치료를 중재로 한 연구, 사용한 한약의 구성 약재를 명시하지 않은 연구이다.
2. 데이터베이스 및 검색 방법
2014년 1월부터 2018년 12월까지 발표된 논문을 대상으로 중국의 전자 데이터베이스 검색 사이트인 중국 학술정보원 (China National Knowledge Infrastructure, CNKI)를 활용하여 연구 검색을 시행하였다. 검색은 2019년 7월 3일에 실시하였으며, 논문 선별을 위한 검색어로 아토피 피부염을 의미하는 ‘特应性皮炎’와 ‘异位性皮炎’를 사용하였다. 검색 범위는 Medicine & Public Health 내에서 Traditional Chinese Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herbs, Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine with Western Medicine 3가지 영역으로 한정하였다.
3. 연구 선택 및 자료 추출
독립된 2명의 연구자(YGJ, KSJ)가 선정 및 제외 기준에 따라 검색된 논문의 제목과 초록을 검토하여 일차적으로 연구를 선별하였다. 그 후, 일차적으로 제외하고 남은 문헌은 2명의 독립된 연구자(YGJ, KSJ)가 선정 및 제외 기준을 적용하여 전문 검토를 통해 이차적으로 연구를 선별하였으며, 이견 발생시 연구자간 논의를 통해 최종적으로 문헌을 선정하였다. 최종 선정된 연구에서 출판 연도, 연구 대상자 특성, 연구 설계 및 중재, 처방된 한약 및 본초, 변증 유형, 평가항목 및 결과 등의 자료를 추출하였다.
4. 연구의 질 평가
본 연구에서는 선정된 무작위 대조군 임상 연구의 질을 평가하기 위하여 Jadad Scale11)을 사용하였다. Jadad Scale은 무작위 배정, 이중 맹검, 탈락 보고 여부로 구성된 3가지 항목에 대해 각각 0, 1, 2점의 점수를 매긴 후 총점을 합하여 무작위 대조군 임상 연구의 질을 평가하는 척도이다. 총 5점 만점으로, 0~2점은 연구의 질이 low quality로 3~5점은 high quality로 평가된다. 평가에 있어 의견불일치가 발생한 경우 제 3의 다른 연구자와 함께 재논의하였다.
결 과
1. 검색결과
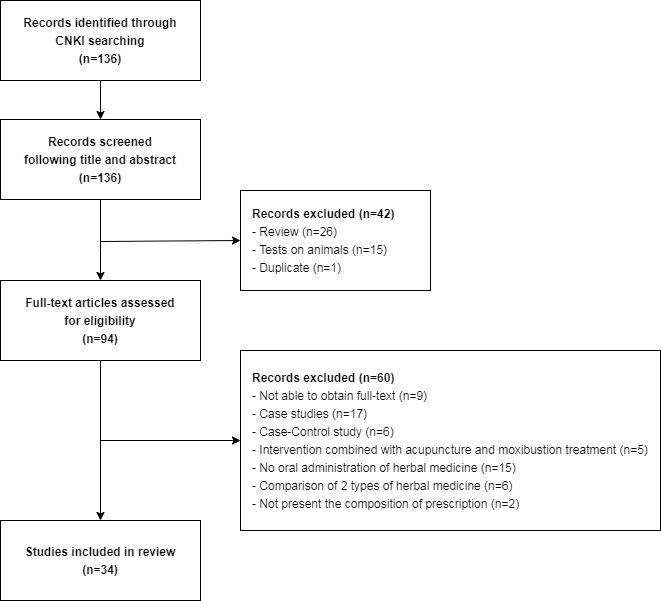
CNKI를 이용하여 2014년 1월부터 2018년 12월까지 발표된 문헌 중 검색한 결과 총 136편이 수집되었다. 논문들의 제목과 초록을 검토하여 문헌 연구(review)이거나, 동물을 대상으로 한 연구이거나, 중복된 경우를 제외하여 1차로 42편을 배제하였다. 이후 선별된 94편의 논문을 대상으로 전문을 검토하여 원문이 존재하지 않거나, 환자-대조군 연구이거나, 증례군 및 증례 연구이거나, 침구 치료를 중재로 하였거나, 치료군이 한약을 경구 복용하지 않았거나, 대조군에 경구 한약 치료를 중재로 하였거나, 사용한 한약의 구성 약재를 명시하지 않은 연구를 제외하여 최종적으로 34편의 논문이 본 연구의 분석 대상으로 선정되었다(Fig. 1).
총 34편의 선정된 문헌을 출판연도 순으로 자료를 수집하였다. 각 문헌별 중재로 사용된 치료 방법에 따른 연구 설계 (Table 1)를 비롯하여 연구 대상의 인구통계학적 정보, 유병기간, 치료방법, 치료기간, 추적기간, 평가 지표 및 평가 결과, 안전성에 관한 정보를 추출하였다 (Table 2). 각 연구에서 한약 경구 복용에 활용된 변증 및 사용된 한약 처방의 구성은 별도로 기재하였으며 (Table 3), 그 처방들의 구성 약재들을 빈도 별로 정리하였다 (Table 4).
2. 선정된 연구 분석
분석에 포함된 총 34편 논문의 출판 연도를 살펴보면, 2014년 9편, 2015년 5편, 2016년 5편, 2017년 7편, 2018년 8편으로 2014년에 출판된 논문이 9편으로 가장 많았다.
각 연구에서 모집한 대상자 수는 최소 48명에서 최대 180명으로 다양하였다. 대상자 수에 따른 연구의 수를 분석한 결과, 48명에서 60명을 대상으로 한 연구는 6편, 61명에서 80명을 대상으로 한 연구는 11편, 81명에서 100명을 대상으로 한 연구는 8편, 101명에서 120명을 대상으로 한 연구는 5편, 121명에서 180명을 대상으로 한 연구는 4편이었다. 연구 대상자의 나이를 분석한 결과, 만 2세부터 80세까지 소아, 청소년 및 성인을 모두 포함하여 특정 연령대만을 대상으로 하지 않은 연구가 22편이었다. 이와 달리 만 2세에서 16세 사이의 소아 및 청소년으로 한정한 연구는 10편이었으며, 만 18세 이상의 성인을 대상으로 한 연구는 2편이었다. 포함된 연구 대상자의 아토피 피부염에 대한 병정 기간은 34편의 연구 중 20편에서 언급되었으며, 병정 기간의 범위는 최소 1일에서 최대 35년으로 다양하였다.
각 연구에서 설정한 치료 기간을 살펴보면 중재 기간이 2주 이상 4주 미만인 연구는 6편, 4주 이상 8주 미만인 연구는 19편, 8주 이상 12주 이하인 연구는 9편이었다. 선정된 34편 연구의 임상시험 설계 형태를 분석한 결과 34편 연구 모두 치료군 뿐만 아니라 대조군에도 위약이 아닌 한의학 혹은 서양의학적 치료를 시행하는 형태였다.
치료군에 시행된 중재 형태를 구체적으로 살펴보면 34편의 연구 중 10편은 한약 경구 복용을 단독으로 하였으며, 24편의 연구는 한약 경구 복용과 함께 기타 치료가 병행되었다. 24편의 연구에서 병행된 치료를 살펴보면 1편에서는 한방 외용제와 서양의학적 치료가 함께 사용되었고, 13편에서는 서양의학적 치료가 병행되었으며, 10편에서는 한방 외용제가 사용되었다.
총 11편의 연구에서 치료군 중재에 병용된 한방 외용제의 사용 방법은 드레싱 요법(10회)과 보습 요법(1회)의 형태로 나뉘었다. 드레싱 요법의 구체적 형태는 龍牡湯이 세척(2회), wet-dressing(1회), 세척/습포/wet-dressing(1회)의 방법으로 사용되었으며, 이외에도 自擬皮炎合劑 세척(1회), 甘草潤膚洗劑 세척(1회), 膚悅康洗劑 세척(1회), 10% 황백 용액 습포(1회), 濕疹散 드레싱(1회), 中藥 외용제(苦参, 黄芩, 金銀花, 蒲公英, 地肤子) 熏洗/擦涂/外敷(1회)가 제시되었다. 보습 요법엔 오일 형태인 複方甘草油(1회)가 사용되었다. 또한 총 14편의 연구에서 치료군에 병행된 서양의학적 치료의 종류별 사용 횟수를 중복을 허용하여 분석해 본 결과, 항히스타민제 7회, 스테로이드제 5회, 보습제 4회, 면역억제제 3회, 항소양제 1회, Vitamin C 1회 사용되었다.
대조군에 시행된 중재를 치료 형태에 따라 복용제와 외용제로 나누어 분석해본 결과 복용제는 34편 모두에서 사용되었고 항히스타민제가 32회, Vitamin C 4회, 경구용 스테로이드제가 2회, Compound glycyrrhizin 1회 투여되었다. 또한 외용제 치료는 34편 중 20편의 연구에서 시행되었으며 스테로이드제 10회, 보습제 6회, 면역억제제 3회, 한방 외용제 2회, 항소양제 1회, 소염제가 1회 사용되었다.
3. 처방 및 본초 분석
치료군에 경구 투여된 한약 처방의 종류를 분석한 결과 총 34편의 연구 중 33편에서 복합 약재로 이루어진 처방을 사용하였으며, 1편의 연구에서는 단미 처방을 사용하였다. 복합 처방의 빈도를 살펴보면 龍牡湯을 투여한 연구가 5편으로 가장 많았으며, 健脾養血祛風湯은 2편, 加味滋陰除濕湯, 祛風利濕合劑, 健脾祛風湯, 健脾安神方, 健脾養血湯, 健脾潤膚湯, 健脾潤膚膏方, 健脾止癢湯, 健脾化濕中藥, 健脾化濕導滯的自擬中藥方, 健脾化濕法擬方, 當歸飲子, 補脾祛風方, 四君子湯, 潤燥祛風湯, 養血潤膚飲合五苓散加減, 胃芩湯, 育陰化濕湯, 自擬皮炎合劑, 地芍玄烏湯, 清熱利濕宣肺湯, 解毒潤膚湯, 紅花逍遙片은 각 1편의 연구에서 사용되었다. 1편의 단미 처방을 투여한 연구에서는 馬齒莧을 水煎液 하였다. 복합 처방을 구성하는 단일 본초의 사용 횟수를 정리한 결과, 茯苓이 총 25회로 가장 많이 사용되었다. 그다음으로는 生地黃, 白朮, 白鮮皮, 甘草, 當歸, 地膚子, 防風, 黃芪, 蒼朮 순으로 24회에서 11회 사이로 사용되었다. 이외 본초의 사용 횟수는 표(Table 4)로 정리하였다.
4. 변증 유형 분석
본 논문에 포함된 34편의 연구 중 11편은 변증이 제시되지 않았으나 23편의 연구에서는 연구 대상자 모집 시 아토피 피부염을 한의학적 변증 기준에 따라 나누어 모집하였다. 하나의 변증 유형에 해당하는 환자만 대상으로 한 연구도 있었으며 여러 변증 유형의 환자를 동시에 모집한 연구도 있었다. 한의학적 변증 유형을 이용한 23편의 연구 중 가장 많이 언급된 변증 유형은 血虛風燥로 13편의 연구에서 사용되었다. 그다음으로는 風濕蘊膚 5편, 脾虛濕蘊 3편, 濕熱蘊結, 陽虛血燥, 熱胎, 脾濕 각 2편, 血虛, 脾虛, 脾虛血燥, 濕熱, 風熱加濕, 脾虛失運, 濕熱蘊盛 각 1편에서 사용되었다.
변증 유형 중 가장 많이 언급된 血虛風燥型, 風濕蘊膚型, 脾虛濕蘊型 환자를 모집한 연구를 대상으로 각 변증 유형별로 사용된 처방을 분석하였다. 그 결과 血虛風燥型 환자를 대상으로 한 13편의 연구 중 5편에서는 龍牡湯, 2편에서는 健脾養血祛風湯이 사용되었으며 加味滋陰除濕湯, 當歸飲子, 養血潤膚飲合五苓散加減, 胃芩湯, 自擬皮炎合劑, 紅花逍遙片은 각 1편에서 사용되었다. 風濕蘊膚型 환자를 대상으로 한 5편의 연구 중 2편에서는 龍牡湯이 사용되었으며 加味滋陰除濕湯, 祛風利濕合劑, 胃芩湯은 각 1편에서 사용되었다. 脾虛濕蘊型 환자를 대상으로 한 3편의 연구에서는 龍牡湯, 健脾化濕方, 健脾化濕法擬方이 각 1편에서 사용되었다.
같은 변증 유형이라 하더라도 연구에 따라서 사용된 처방이 상이한 경우가 많았다. 血虛風燥型, 風濕蘊膚型, 脾虛濕蘊型 환자에게 투여된 처방의 본초 구성을 분석하여 각 변증 유형의 본초별 사용 횟수를 세었다. 血虛風燥型 환자를 대상으로 한 13편의 연구에서 투여된 처방에서는 生地黃이 11회로 가장 많이 사용되었고 當歸가 8회, 骨碎補, 牡蠣, 龍骨이 각 6회 사용되었다. 風濕蘊膚型 환자를 대상으로 한 5편의 연구에서 투여된 처방에서는 白鮮皮, 茯苓이 각 5회, 薏苡仁이 3회 사용되었다. 脾虛濕蘊型 환자를 대상으로 한 3편의 연구에서 투여된 처방에서는 白鮮皮, 白朮, 生地黃, 地膚子, 蒼朮이 각 3회 사용되었다.
5. 평가항목 및 치료 결과 분석
아토피 피부염의 증상과 치료 효과를 평가하기 위해서 다양한 방법이 사용되었는데 34편의 연구 중 1편은 Total IgE 수치만 측정하였으며, 1편은 SCORAD index(SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index)만 평가하였다. 그 외 32편의 연구에서는 아토피 피부염 증상의 개선 정도에 따라 등급화하여 치료에 대한 유효성 평가를 시행하였다. 28편에서는 痊癒(Cured), 顯效(Significant effect), 有效(Effective), 无效(Invalid)로 나누었으며, 4편에서는 顯效(Significant effect), 有效(Effective), 无效(Invalid)로 나누었으며, 1편에서는 治愈(Cured), 好转(Improved), 未愈(Invalid)로 나누었다. 나누어진 등급을 바탕으로 총 유효율(Total Effective Rate, TER)은 전체에서 无效(Invalid)만 제외하여 (Total case - Invalid case) / (Total case) × 100%로 계산하였고, 유효율(Effective Rate, ER)은 痊癒(Cured)와 顯效(Significant effect)의 수를 더하여 (Cured case + Significant effect case) / (Total case) × 100%로 계산하였다. 총 유효율(TER)을 계산하여 치료 효과를 평가한 연구는 23편이며, 유효율(ER)은 10편에서 평가되었으며, 둘 다 사용한 연구는 1편이었다.
이외 기타 사용된 평가 지표들을 다빈도 순으로 정리한 결과 SCORAD index(SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index) 14편, Total IgE 수치 측정과 치료 후 재발률 조사 각 7편, 삶의 질 평가는 6편에서 사용되었다. 또한 EASI(Eczema Area and Severity Index), Eosinophil count, IL-4, VAS(Visual Analogue Scale), 부작용 발생률은 각 3편에서 평가되었다.
선정된 연구 중 총 유효율(TER)이나 유효율(ER)을 사용한 32편 모두에서 p value를 제시하였다. 총 유효율을 제시한 23편의 연구에서 치료군의 총 유효율이 대조군의 총 유효율에 비하여 높다고 보고하였으나, 그 중 2편의 연구는 p value가 0.05 이상인 경우로 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다. 유효율을 제시한 10편의 연구는 치료군의 유효율이 대조군의 유효율보다 통계적으로 유의하게 높았다(p < 0.05). 또한, SCORAD index를 평가지표로 활용한 14편의 연구 중 13편에서 치료군이 대조군에 비해 SCORAD 점수 개선에 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보인다고 보고하였으나(p < 0.05), 나머지 1편의 연구에서는 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다(p >0.05).
6. 안전성 평가
선정된 연구 중 13편의 연구에서 부작용에 대하여 언급하였다. 치료군은 13편 중 2편에서는 부작용이 발생하지 않았다고 보고되었으며, 나머지 11편에서 발생한 부작용으로는 피부 불편감, 알러지 반응, 발적, 가려움, 경도의 위장관 반응, 오심, 위장장애, 설사, 복부팽만, 복통, 변비, 구토, 입마름이 총 40건 발견되었다. 대조군 또한 13편 중 2편에서는 부작용이 발생하지 않았다고 보고되었으나 나머지 11편에서 총 70건의 부작용이 발생하였다. 대조군의 부작용으로는 치료군처럼 경도의 위장관 반응, 오심, 구토, 복통, 위장관 장애, 알러지 반응, 피부 불편감, 가려움, 입마름이 보고되었을 뿐 아니라 여드름, 졸림, 두통, 어지럼증, 피로, 생리불순, 혈압 증가, 집중 불가, 간 기능 이상도 발생하였다.
7. 연구의 질 평가
선정된 연구의 Jadad scale을 분석한 결과 35편 모두에서 무작위 배정을 시행하였으며, 그중 9편에서 무작위 배정 방법에 대한 언급이 있었다. 탈락과 중도 포기에 관한 내용이 있거나 혹은 참여자 및 연구자의 눈가림에 관해 기술한 논문은 각 1편이었다. Jadad 점수가 4점인 논문이 1편, 3점인 논문이 1편, 2점인 논문이 7편, 1점인 논문은 25편이었다.
고 찰
아토피 피부염은 심한 가려움증과 함께 홍반, 삼출, 인설, 가피, 태선화 등의 증상을 가지는 만성 염증성 피부 질환이다1). 아토피 피부염의 발생 초기에 증상의 적절한 관리가 이루어지지 않으면 아토피 피부염의 증상은 삼출을 동반한 홍반성 발진의 형태인 아급성 병변을 거쳐서 태선화가 발생한 만성 병변으로 진행된다45). 또한 아토피 피부염 환자는 피부 증상뿐 아니라 다양한 심리적, 사회적 스트레스를 경험하며 심리적 스트레스는 불면, 자살 충동, 사회적인 고립 등을 유발하여 이는 결국 아토피 피부염의 악화인자로 작용한다46). 아토피 피부염의 발생은 유전학적 인자, 환경적 인자, 심리적 인자, 면역학적 인자 등과 같이 여러 요인이 상호작용하여 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있으나, 현재까지 아토피 피부염의 명확한 원인은 밝혀지지 않고 있다5,46).
대부분의 아토피 피부염은 T세포의 비정상적인 작용 및 IgE 항체 증가와 연관된 면역학적 이상으로 발생한다47). T세포는 발현되는 cytokine에 따라 Th1(T-helper cell type 1)과 Th2(T-helper cell type 2)로 분화되어 면역 반응을 유발한다. Th1은 IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α 등의 cytokine을 분비하여 대식세포를 활성화하는 반면 Th2는 IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13 등의 cytokine을 분비하여 IgE, 호산구, 비만세포에 의한 면역반응을 유발한다. 일반적으로 아토피 피부염은 Th2가 비정상적으로 활성화되어 Th1을 억제하는 질환으로 알려져 있으나, 아토피 피부염의 병기에 따라 Th1과 Th2의 활성이 달라진다는 것이 제시되고 있다. 즉, 아토피 피부염은 급성 병기의 피부조직에서는 Th2 면역 반응이 우세하는 환경이지만, 만성 병기에서는 Th1 면역 반응의 지배적 환경이 조성된다48).
아토피 피부염은 한의학적으로 奶癬, 四彎風, 胎㾾瘡, 血風瘡, 濕瘡, 浸淫瘡 등의 범주에 해당하며, 선천적으로 濕熱內醞한 상태에서 피부를 통하여 風濕熱邪가 침범하게 되어 발생한 것으로 본다8). 한의학에선 아토피 피부염을 증상의 진행 상태에 따라 급성기는 濕熱, 아급성기는 脾虛濕盛, 만성기는 陰虛血燥로 변증하여 분류한다49). 2015년에 개정된 아토피 피부염 한의임상진료지침8)에선 아토피 피부염을 진행 상태가 아닌 발병 시기에 따라 유아 및 아동은 濕熱, 胎熱, 脾虛風燥로, 성인은 風濕蘊膚, 濕熱互結, 脾虛濕蘊, 血虛風燥로 변증하기도 하였고, 변증 유형별로 淸熱解毒, 活血祛風, 建脾化濕, 養血潤膚 등의 치법을 제시하였다.
본 연구는 중국의 가장 대표적 데이터베이스인 CNKI에서 아토피 피부염을 의미하는 特应性皮炎과 异位性皮炎으로 검색하여 최근 5년간 발표된 아토피 피부염의 한약 치료에 대한 논문을 선별하였다. 근거 수준이 높은 연구를 포함하기 위해 분석 대상은 무작위 대조군 임상 연구로 한정하였고, 그 결과 34편이 조건에 부합하였다.
치료군에 시행된 중재로서 한약 경구 복용만을 단독으로 한 연구는 총 34편의 연구 중 10편이었으며, 그외 24편의 연구에서는 한약 경구 복용과 함께 다른 치료가 병행되었다. 24편의 연구에서 사용된 병행 치료를 종류별로 분석한 결과 최소 1가지부터 최대 3가지의 기타 치료가 병행되었으며, 한방처방을 기초로 제조한 외용제(11회), 항히스타민제(7회), 스테로이드제(5회), 보습제(4회), 면역억제제(3회) 등이 병용되었다. 그중 한방 외용제는 방법에 따라 드레싱 요법(10회)과 보습 요법(1회)으로 사용되며 가장 많이 사용된 처방은 龍牡湯으로 세척, 습포, wet-dressing 등의 방식이 제시되었다.
치료군에 경구 투여된 한약 처방의 종류를 분석한 결과, 단미 처방인 馬齒莧水煎液을 복용한 1편을 제외한 33편은 복합 약재로 이루어진 처방을 사용하였으며 복합 처방의 종류는 총 25가지였다. 사용된 처방을 빈도순으로 살펴보면 龍牡湯이 5편으로 가장 많았으며, 그다음으로는 健脾養血祛風湯 등이 사용되었다. 복합 처방을 구성하는 단일 본초의 사용 횟수를 정리한 결과 茯苓(25회), 生地黃(24회), 白朮(22회), 白鮮皮(21회) 등이 아토피 피부염의 변증 유형을 막론하고 다용되었다.
茯苓은 生津, 潤燥, 利水渗濕의 효능을 지니며50), 주요 성분인 β-glucan과 triterpene은 조직의 재생과 치유기능, 항산화 및 항염증 등의 효과를 나타내는 것으로 보고된다51). 生地黃은 한의학적으로 淸熱凉血, 養陰生津의 효능을 가진 약재로 血熱妄行으로 나타나는 각종 風燥 증상에 사용되어 왔으며50), 항염증과 항알레르기52) 및 항산화 작용53)이 보고된 바 있다. 生地黃은 mast cell, eosinophil, IgE의 수치를 감소시키며54), IL-4, TNF-β 등 생성 억제52) 및 COX-2 유전자 발현을 조절하여55) 아토피 피부염에 효과적임이 밝혀졌다. 白朮은 補脾益氣, 燥濕利水의 효능을 가지고 있어 임상적으로 脾胃虛寒과 水濕停滯로 인한 다양한 질환에 활용되어 왔으며50), 염증 치료의 가능성이 있는 약재이다56). 白鮮皮는 피부 질환 치료에 자주 쓰이는 약재로 淸熱燥濕의 효능을 가지며 濕熱瘡毒, 濕疹, 風疹, 疥癬瘡癩 등의 치료에 사용되어 왔다50). 白鮮皮는 세포 내 다양한 염증 조절인자의 생성에 관여하여 항염증57) 및 항알레르기 작용58)을 나타냄이 보고된 바 있다. 위와 같이 茯苓과 生地黃은 한의학적으로 生津의 효능을 지니며, 白朮과 白鮮皮는 燥濕의 효능을 가지는 약재로서 항염증 및 항알레르기 효과를 나타내어 변증 유형을 막론하고 아토피 피부염의 치료에 많이 활용된 것으로 생각된다.
한의학적 변증이 제시된 23편의 연구에서는 아토피 피부염을 한의학적으로 변증하여 그 유형에 따라 대상 환자를 모집하였다. 하나의 변증 유형에 해당하는 환자만 대상으로 한 연구도 있었으며 여러 변증 유형의 환자를 동시에 모집한 연구도 있었다. 가장 많이 언급된 변증 유형은 13편에서 사용된 血虛風燥型이었으며, 그다음으로는 風濕蘊膚型 5편, 脾虛濕蘊型은 3편에서 사용되었다.
아토피 피부염에서 血虛風燥型은 주로 만성화된 피부염의 형태로서 환부가 비후하고 건조하며 조흔, 혈가, 태선화 및 극렬한 소양감을 특징으로 한다8). 血虛風燥型의 치법으로는 養血潤膚를 사용하며, 주로 陰血을 관장하는 肝腎을 補하고 津液을 보충하여 건조해진 피부를 滋潤하는 처방을 사용한다8). 血虛風燥型 아토피 피부염 처방에 다빈도로 사용된 약재는 生地黃(11회)을 비롯하여 當歸(8회), 骨碎補, 牡蠣, 龍骨(각 6회) 이었다.
當歸와 骨碎補는 한의학적으로 活血의 효능을 지닌 약재로서 항염증 효과가 있다고 알려져 있다59,60). 龍骨과 牡蠣가 함께 포함된 처방은 정신불안, 불면, 갱년기 증후군 등의 치료에 활용되어 정신과적 임상 효능이 주로 보고되는 바이다61). 이를 통해 추론해보건대 血虛風燥型 아토피 피부염은 증상이 만성화된 단계로서 환자가 호소하는 신체 증상뿐 아니라 정신적 스트레스 또한 아토피 피부염의 주 악화 요인으로 작용할 수 있으므로 龍骨과 牡蠣를 응용한 것으로 생각해볼 수 있다.
風濕蘊膚型 아토피 피부염은 皮疹이 얼굴과 사지에 항상 존재하고 구진이 건조되어 떨어지게 되며, 口腔乾燥, 目赤, 大便秘結 등의 증상을 수반한다8). 특히나 다용된 茯苓과 薏苡仁은 利水渗濕의 효능을 통해 피부에 울체된 風濕을 해소하여 염증을 개선하는 방향으로 활용된 것으로 생각된다. 또한, 脾虛濕蘊型의 아토피 피부염은 만성적인 재발성의 소양감을 지니며 동반 증상으로는 顔色蒼白, 身疲乏力, 飮食減少, 腹脹便糖 등이 있다8). 다빈도로 사용된 약재인 地膚子와 蒼朮은 濕邪를 제거하여 항염증 작용 및 동반 증상을 개선하는 방향으로 활용된 것으로 생각된다.
종합적으로 경구 복용하는 한약과 한방 외용제로 가장 많이 사용된 처방은 龍牡湯으로 龍骨, 牡蠣, 骨碎補, 生地黃 등으로 구성된다. 이는 가장 많이 언급된 변증 유형인 血虛風燥型 처방에 사용된 다빈도 본초와 비슷한 경향성을 가지는 것으로 판단되며, 龍牡湯이 사용된 5편 전부에서 변증으로 血虛風燥가 선택된 것과 연관된다.
아토피 피부염의 증상과 치료 효과를 평가하기 위하여 다양한 방법이 사용되었는데 총 34편의 연구 중 32편은 아토피 피부염 증상의 개선 정도에 따라 등급화하여 치료에 대한 유효성 평가를 시행하였다. 주요 평가 지표로는 총 유효율(23편)과 SCORAD index(14편), 유효율(10편)이 있었다. 이외에도 치료 후 재발률, Total IgE(각 7편), 삶의 질(6편) 등이 평가되었다.
선정된 연구의 치료 결과를 살펴보면 총 유효율을 제시한 23편의 연구 중 21편에서 치료군의 총 유효율이 대조군의 총 유효율에 비하여 통계적으로 유의한 결과가 도출되었다. 또한, SCORAD index를 평가지표로 활용한 14편의 연구 중 13편에서 치료군이 대조군에 비해 SCORAD 점수 개선에 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였다.
안전성 평가를 시행한 결과 13편의 연구에서 부작용을 보고하였으나, 치료군은 대조군과 비교하여 유의하게 적은 수의 부작용이 발견되었다. 이는 아토피 피부염을 개선하는 데 한약을 경구 복용하는 것이 보다 안전하고 효과적이라는 근거자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
이상으로 최근 5년간 아토피 피부염에 한약 치료를 시행한 중국 내 무작위 대조군 임상 연구를 정리하였다. 본 연구는 변증 및 사용된 본초를 중점적으로 분석하였으며 아토피 피부염에 한약 경구 복용을 포함한 중재가 그렇지 않은 중재에 비하여 유의한 효과와 안전성이 있음을 보여주었다.
다만, 본 연구의 한계는 다음과 같다. 첫째로, 검색원을 CNKI에 국한하여 중국의 논문만을 분석하였으므로 결과를 일반화하기 어려웠다. 둘째로, 대부분의 연구에서 아토피 피부염의 증상 개선에 따라 등급화하여 평가 지표로 활용하였으나 연구마다 그 기준에 차이가 있었다. 셋째로, 무작위 배정 방법을 언급한 논문은 9편뿐이었으며 참여자 및 연구자의 눈가림 혹은 탈락과 중도 포기에 관해 기술한 논문은 각 1편에 불과했다. 이러한 한계점을 보완하기 위하여 향후 중국의 기타 데이터베이스와 다른 국가들의 관련 연구까지 분석하여 본다면 아토피 피부염의 치료에 대한 이해를 높일 수 있을 것으로 사료된다. 이와 더불어 관찰 연구, 증례 보고, 실험 연구 등까지 영역을 넓혀서 더 많은 수의 문헌을 대상으로 한 고찰도 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
현재까지 아토피 피부염의 한약 치료에 대한 국내의 무작위 대조군 연구는 대다수가 한방 외용제를 중재로 한 연구로서 한약을 경구 복용한 무작위 대조군 연구는 다소 부족한 실정이다10). 따라서 한약을 이용한 무작위 대조군 임상 연구가 활발히 이루어지고 있는 중국의 연구를 분석하여 치료 효과 및 안전성을 평가하였다는 데 본 연구의 의의가 있다고 볼 수 있다. 향후 적절한 무작위 배정 방법과 이중 맹검을 사용하여 비뚤림을 최소화함으로써 방법론상의 문제점을 보완한 양질의 임상 연구들이 수행되어야 할 것이며, 그를 바탕으로 아토피 피부염 치료의 한의학적 근거 마련에 본 연구가 기반이 되기를 기대한다.
결 론
본 연구는 중국의 데이터베이스 검색 사이트인 CNKI에서 검색을 통해 최근 5년간(2014년~2018년) 발표된 아토피 피부염의 한약 치료에 대한 무작위 대조군 임상 연구 논문 34편을 분석하여 다음과 같은 결과를 얻었다.
치료군에 한약 경구 복용만을 단독으로 한 연구는 34편의 연구 중 10편이었으며, 24편은 한약 경구 복용과 함께 최소 1가지부터 최대 3가지의 기타 치료가 병행되었다. 한방 외용제(11회)가 가장 많이 병용되었으며, 龍牡湯이 세척, 습포, wet-dressing 등의 방식으로 다용되었다.
치료군에 경구 투여된 한약 처방의 종류를 분석한 결과, 1편에서는 단미 처방인 馬齒莧水煎液을 복용하였다. 그 외 33편에서는 복합 약재로 이루어진 처방 25가지가 사용되었으며 龍牡湯이 5편으로 가장 많았다. 복합 처방을 구성하는 단일 본초를 정리한 결과 茯苓(25회), 生地黃(24회), 白朮(22회), 白鮮皮(21회) 등이 아토피 피부염의 변증 유형을 막론하고 다용되었다.
한의학적 변증이 제시된 23편 중 가장 많이 언급된 변증 유형은 13편에서 사용된 血虛風燥型이었으며, 그다음으로는 風濕蘊膚型 5편, 脾虛濕蘊型은 3편에서 사용되었다. 血虛風燥型 아토피 피부염 처방에 다빈도로 사용된 약재는 生地黃(11회)을 비롯하여 當歸(8회), 骨碎補, 牡蠣, 龍骨(각 6회) 이었다.
아토피 피부염 증상의 개선 정도에 따라 등급화하여 치료에 대한 유효성 평가를 시행한 연구는 32편이었다. 주요 평가 지표로는 총 유효율(23편)과 SCORAD index(14편), 유효율(10편)이 있었다. 이외에도 치료 후 재발률, Total IgE(각 7편), 삶의 질(6편) 등이 평가되었다.
평가 지표로 총 유효율과 SCORAD index를 활용한 대부분의 연구에서 치료군이 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의하게 좋은 결과를 보였다. 안전성 평가 결과, 치료군은 대조군과 비교하여 유의하게 적은 수의 부작용이 발견되었다. 이는 아토피 피부염 치료에 한약 경구 복용이 효과적이고 안전하다는 근거 및 연구 설계의 기초 자료가 될 수 있을 것이다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 2019년도 정부 (미래창조과학부)의 재원으로 한국연구재단 바이오 의료기술개발사업의 지원을 받아 이루어진 것임(No.NRF-2015M3A9E3051054).
References
- Lee HS, Kim JS, Pyun BY. Changes of the Prevalence and the Allergens of Atopic Dermatitis in Children: In between the Year of 1992 and 2002. Korean Acad Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2002;12(4):263-71.
- Oh JW. Recent Situation of the Management of Atopic Dermatitis. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;32(1):14-5.
- Hwang ML, Ahn JH, Jea HK, Kim SY, Jung HA. Characteristics of Clinical Trials in Korea for Atopic Dermatitis. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatology. 2019;32(2):68-93.
-
Son HK, Kim HS. A Comparative Study of Family Management Style According to Severity of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Child Heal Nurs Res. 2016;22(4):309-16.
[https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2016.22.4.309]

-
David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic Dermatitis: Pathophysiology. Vol. 1027, Advances in experimental medicine and biology. Springer, Cham; 2017. 21-37.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64804-0_3]

- Han TY, Na CH, Lee JH, Kim HO, Park CO, Seo YJ, et al. Treatment of atopic dermatitis. Korean J Dermatology. 2018;56(10):581-93.
-
Mooney E, Rademaker M, Dailey R, Daniel BS, Drummond C, Fischer G, et al. Adverse effects of topical corticosteroids in paediatric eczema: Australasian consensus statement. Australas J Dermatol. 2015;56(4):241-51.
[https://doi.org/10.1111/ajd.12313]

- Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. KMCPG-Atopic dermatitis. 1st rev. Daejeon; 2014. 26-32.
- Lee S, Yoon H, Ko W. Recent Trend and Proposal for Acupuncture Clinical Trial on Atopic Dermatitis. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatology. 2017;30(3):76-87.
-
Park H, Kwon J, Yoo J. Quantity and Quality Assessment of Randomized Controlled Trials in the Atopic Dermatitis. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatology. 2014;27(4):45-57.
[https://doi.org/10.6114/jkood.2014.27.4.045]

- Zhao T, Yu X, Xie Y. Research on atopic dermatitis in children treated with the method of invigorating spleen and eliminating dampness. Clin Res Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;6(15):65-7.
- Liu X. Clinical observation of 38 cases of atopic dermatitis treated with Longmu decoction. Inn Mong Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;16.
- Fu W. The Observation of the Curative Effect of Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Chinese Foreign Med Res. 2014;12(18):12-4.
- Zhou A, Ji A, Shi C, Gao L. Treating 30 Cases of Atopic Dermatitis in Children by the Method of Invigorating Spleen to Eliminate Dampness. West J Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;27(8):73-4.
- Wang J, Xi W, Tong X, Liu C. Detoxification Moisturizing Decoction in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Inf Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;31(5):111-3.
- Chen B. Clinical Efficacy of Yangxue Jianpi Runfu Method in Treating Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and Its Influences on Serum Levels of Interleukin-18. Chinese J Dermatovenereology Integr Tradit West Med. 2014;13(5):283-5.
- Hu X. Clinical Effect of Longmu Soup in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. CHINA JOURNAL CHINESE Med. 2014;29(198):1674-6.
- Zhu H. Clinical study on self-made dermatitis mixture for atopic dermatitis. nner Mong Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;(34):1-2.
- Wang H, Liu H, Wang Z. Therapeutic effect of Chinese herbal medicine of strengthening the spleen and soothing the nerves on atopic dermatitis. Jilin J Tradit Chinese Med. 2014;34(12):1255-7.
- Yang Y. Study on Clinical Effect of TCM Intervention in Treating Blood Deficiency and Wind Dryness Type Atopic Dermatitis. Guangming J Chinese Med. 2015;30(4):753-5.
- Li X. Effect of Chinese Medicine in Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. China Heal Stand Manag. 2015;6(19):140-1.
- Zou J. Clinical Study on Jianpizhiyang Decoction Effect in Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. China Contin Med Educ. 2015;7(22):166-7.
- Su C, Wu Z, Zhong J, Huang T, Xu Z, Yue T. Effects of Honghua Xiaoyao Tablet on immune factors in patients with atopic dermatitis due to blood deficiency and wind-dryness. Pract Clin J Integr Tradit Chinese by West Med. 2015;15(10):10-3.
- Song F. Clinical Observation on Jianpi Yangxue Decoction in Treating Atopic Dermatitis. Shenzhen J Integr Tradit Chinese by West Med. 2015;25(22):51-2.
- Yu J, Wang Q, Li Y. Observation on the Therapeutic Effect of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine on Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Chinese J Tradit Med Sci Technol. 2016;23(2):219-20.
- Liu L. Study on Purslane Decoction to Reduce the Total Serum IgE Level of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Sichuan Med J. 2016;37(7):807-8.
- Wang J. Treatment of 45 cases of atopic dermatitis with self-made Dixuanwu Decoction. Integr Tradit Chinese West Med Chinese Med. 2016;20(30):4260-1.
- Lyu H, Hua H, Zheng W, Sun F, Yu X. The effect of modified Ziyin Chushi decoction on children with atopic dermatitis. Mod Chinese Clin Med. 2016;23(6):36-8.
- Lyu H, Feng J, Wang Q, Zhang H, Yu X. Efficacy of Yuyin Huashi Decoction on Children with Chronic Atopic Dermatitis and Effects on IL-4 and INF-γ. J Shandong Univ Tradit Chinese Med. 2016;40(6):521-3.
- Zhao C. Observation on Therapeutic Effect of TCM Syndrome Differentiation on Atopic Dermatitis. Yunnan J Tradit Chinese Med. 2017;38(1):46-7.
- Shi H. TCM Syndrome Characteristics of Children with Atopic Dermatitis and Clinical Effect of Chinese Herbal Medicine. Guangming J Chinese Med. 2017;32(4):468-70.
- Ouyang Z, Li B, Luo L, Zhao W, Chen Q. Clinical effect of QingreLishiXuanfei decoction in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis with damp-heat accumulation syndrome: an analysis of 30 cases. HUNAN J Tradit CHINESE Med. 2017;33(3):16-8.
- Deng D, Chen H. Longmu Decoction in treating atopic dermatitis in clinical analysis. Nei Mong J Tradit Chinese Med. 2017;(8):5.
- Liu G, Wang Q. Observation on treating AD by TCM medicine umbilical therapy. Clin J Chinese Med. 2017;9(19):123-4.
- Li X, Xu P, Pan W, Zhang H. Clinical research of Qufeng Lishi Mixture in treating fengshi yunfu-type atopic dermatitis. CHINA Med Her. 2017;14(22):101-4.
- Li D. Clinical effectof Jianpi Qufeng Decoction in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. CHINA Mod Med. 2017;24(31):155-7.
- Wang L, Ye J, Yang X. Clinical Efficacy of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction in Treating Patients with Blood Deficiency and Wind Dryness Type Atopic Dermatitis and Its Effect on Skin Barrier Function. Chinese J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. 2018;24(13):178-82.
- Du Y, Liu Y, Tu S, Lin H. Observation of the effect of Jianpi Runfu Decoction combined with compound licorice oil on atopic dermatitis. Nurs Pract Res. 2018;15(4):136-8.
- Lin S, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Wang H. Effect of FuYue Kang Lotion Combined with Bupi Qufeng Prescription on Th17,IL17 and IL-23 in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. ACTA CHINESE Med. 2018;33(238):484-7.
- Wang L, Yang X, Ye J. Clinic curative effect and the influence of LTB 4 LTC 4 of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction in treating Xuexu Fengzao type atopic dermatitis. LISHIZHEN Med Mater MEDICA Res. 2018;29(3):641-3.
- Xie Z. Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment Model of Atopic Dermatitis. World Latest Med Inf. 2018;18(59):137.
- Ye W, Chen M. Clinical effect of spleen-strengthening and moisturizing cream prescription in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: An analysis of 30 cases. HUNAN J Tradit CHINESE Med. 2018;34(8):16-29.
- Zhang L. Clinical observation of Runzao Qufeng Decoction in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. China Pr Med. 2018;13(29):105-7.
- Sun X, You Y, Liu Y, Wang J, Cheng X, Jin C, et al. Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis with Danggui Yinzi and its Immune Function Regulatory Effect. J Chang Univ Chinese Med. 2018;34(6):1153-6.
-
Ryu DH, Oh SR, Jung TS, Ryu DS. The Effect of Angelica gigas Nakai Extract and Bacillus Polyfermenticus KJS-2 on Atopic Dermatitis induced by DNCB in mice. J Korean Med. 2017;38(3):30-42.
[https://doi.org/10.13048/jkm.17023]

-
Noh HM, Park SG, Jo EH, Jang HC, Kim HK, Park HJ, et al. Study about the Comparison of Korean-Western Medicine on Atopic Dermatitis and Psychological Factors. J Physiol Pathol Korean Med. 2018;32(2):113-25.
[https://doi.org/10.15188/kjopp.2018.04.32.2.113]

-
Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105(5):860-76.
[https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.106484]

-
Leung DYM, Soter NA. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(1):S1-12.
[https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2001.109815]

-
Park S, Noh H, Hwang C, Hong S, Park M, Jang HC, et al. Classification of Atopic Dermatitis into Digestive and Respiratory Disorders on the Basis of a Literature Study. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatol. 2016;29(3):106-23.
[https://doi.org/10.6114/jkood.2016.29.3.106]

- National Korean Medicine University Textbook Editing Board. Traditional Herbology. Seoul: Younglimsa; 2010. 228-9.
-
Kim YJ, Park HJ, Lee JS, Do E, Sohn HR, Jeon SM, et al. Antioxidant effect of ethanol extract from Poria cocos depending on cultivation methods. Korea J Herbol. 2016;31(5):107-14.
[https://doi.org/10.6116/kjh.2016.31.5.107.]

-
Kang K, Kim C. Inhibitory Effect of Rehmannia Glutinosa Pharmacopuncture Solution on b-hexosaminidase Release and Cytokine Production via FcRI signaling in RBL-2H3 Cells Kyung-Hwa. J Pharmacopuncture. 2011;14(2):15-24.
[https://doi.org/10.3831/KPI.2011.14.2.015]

- Seo H. The Experimental Study on Anti-inflammation and Anti-oxidation of. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatology. 2008;21(3):104-10.
-
Kim MC, Lee CH, Yook TH. Effects of Anti-inflammatory and Rehmanniae radix Pharmacopuncture on Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice. JAMS J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2013;6(2):98-109.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jams.2012.10.007]

- Kim SB, Kim KJ. The Effects of Rehmannia glutinosa on the Protein Expression Related to the Angiogenesis, Cell Survival and Inflammation. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatology. 2006;19(3):22-33.
-
Hong MH, Kim JH, Bae H, Lee NY, Shin YC, Kim SH, et al. Atractylodes japonica Koidzumi inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines through inhibition of the NF-κB/IκB signal pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2010;33(6):843-51.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0606-6]

- Park J, Shin T, Kim DK, Lee J. The Effects of Dictamni Radicis Cortex on the iNOS Expression and Proinflammatory Cytokines Production. Kor J Pharmacogn. 2011;42(4):348-53.
- Kang H, Lyu J, Lyu S, Kang K, Yoon H, Kim Y, et al. The anti-allergic effects of Dictamni radicis cortex(白鮮皮) on the PMA plus A23187-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. J Korean Orient Med Ophthalmol. 2007;20(1):201-8.
-
Ok S, Oh SR, Jung TS, Jeon SO, Jung JW, Ryu DS. Effects of Angelica gigas Nakai as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent in In Vitro and in Vivo Atopic Dermatitis Models. Hindawi. 2018;2018:1-12.
[https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2450712]

-
Kim YM, Kim EH. The Anti-inflammatory Effect and DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Capability of Rhizoma drynariae Aqueous Extract. Korean J Acupunct. 2015;32(4):169-76.
[https://doi.org/10.14406/acu.2015.026]

- Kim K, Kim W, Kim K. A Study about trends of using Shihogayonggolmoryo-tang granule. KOREAN J Orient Med Prescr. 2012;20(1):159-66.