
Scopolamine으로 유도된 인지장애 마우스의 기억력 개선 효과에 대한 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 추출물의 비교 연구
Ⓒ The Society of Pathology in Korean Medicine, The Physiological Society of Korean Medicine
Abstract
In this study, we investigated the effects of Ginseng Radix (G), Rehmanniae Radix (R), and Fermented red-ginseng extracts (FRG) on cognitive function in scopolamine-induced memory-impaired mice. We measured the effects of G, R, and FRG on the improvement of memory and cognition via behavior analysis. In addition, we measured the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in the hippocampus of each group of mice. The expression of β-amyloid, Tau, and BDNF in the brain tissues were observed through immunohistochemical staining. Ginseng Radix (G) and Fermented red-ginseng (FRG) have effectively improved cognitive function in the water maze test. Ginseng Radix (G), Rehmanniae Radix (R), and Fermented red-ginseng (FRG) have improved the willingness of mice to explore the new environment, as confirmed by Y maze test. In addition, immunohistochemical staining revealed that Ginseng Radix (G) decreased the expression of β-amyloid and Tau in the hippocampus. In addition, fermented red-ginseng (FRG) increased the expression of BDNF. Ginseng Radix (G), Rehmanniae Radix (R), and Fermented red-ginseng (FRG) have decreased the concentration of acetylcholinesterase in the hippocampus as compared with the control group of mice. In conclusion, Ginseng Radix (G), Rehmanniae Radix (R), and Fermented red-ginseng (FRG) are considered to have the potential for development as candidate drugs to control the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Keywords:
Cognitive impairment, Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix, Fermented red-ginseng, Behavioral analysis, AChE activity서 론
노년층의 증가에 따라 퇴행성 질환이 급증하고 있으며, 그중 치매 환자는 더욱이 증가할 것으로 예측되고 있다. 치매 유형 중에서도 가장 흔한 Alzheimer’s disease(AD)의 경우 병태생리가 밝혀지면서 치료제 개발에 대한 많은 연구가 진행되고 있지만 명확한 성과는 현재까지 나타나지 않고 있다1). Alzheimer’s disease는 일반적으로 산화적 스트레스, 아밀로이드의 침착, 과인산화된 Tau 단백질의 응집으로 이뤄진 신경섬유 다발성 병변, 콜린성 신경의 손상, 염증성 인자 등이 발병 원인으로 알려져 있고, 콜린성 신경세포 퇴화로 인한 acetylcholine의 결핍이 주된 원인 중 하나로 알려져 있다2-4).
이를 통해 scopolamine은 체내 acetylcholine 수용체에 대하여 acetylcholinesterase(AChE)의 활성 증가로 신경접합부에 있는 acetylcholine을 분해하여 인지력 감소를 발생시키는 약물로 새로운 항치매 약물의 평가를 위한 시험모델에 많이 사용되고 있다5). Choline의 활성감소로 기억력이 저하되기 때문에 현재까지 Alzheimer’s disease의 대표적 치료 약물로는 cholinesterase inhibitor인 Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine 등이 사용되어 왔으나 효능이 명확히 증명되지 않았고, 여러 부작용을 초래하여 치료에 어려움이 있다6,7). 이러한 문제가 지속됨에 따라 알츠하이머 질환 환자의 기억력과 인지기능을 개선하는 건강기능식품 개발을 위한 천연소재의 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다6).
인삼은 오가피과 Panax속에 속한 다년생 초본으로 그 뿌리를 건조한 것으로, 원기를 보양하고 진액을 생겨나게 하며 안신시켜서 주로 기혈진액이 부족할 때 응용된다8). 생지황은 현삼과에 속하는 다년초로서 현재 건강기능식품 소재의 부원료로 허가되어 기능성 식품소재로서의 활용 가능성이 크며 항산화 및 대사질환에 대한 효과가 보고되었다9).
인삼과 홍삼은 뇌의 노화 방지 및 뇌 혈류량을 증가시키는 것으로 알려져 있어, 인삼의 성분인 Rb1, Rg1, Rg2 등의 주요 사포닌은 전기적으로 기억과 인지능력을 손상시키거나 scopolaminem cycloheximide와 anisodine 등의 약물에 의한 기억력 감소를 유도한 동물실험에서 학습과 기억을 개선시킨다고 보고되고 있다2,10,11).
이에 본 연구에서는 인삼 추출물과 발효공정을 이용하여 기존의 사포닌 성분을 증강시킨 발효홍삼 추출물을 이용하여 인지기능 장애에 대한 효능을 비교하고, 본 교실의 치매모델을 이용한 생지황의 인지개선능에 대한 연구에서 효과를 나타낸 생지황 추출물을 이용하여 scopolamine으로 유도한 기억력 감소모델에서의 기억력 개선 효과를 나타내는지 확인하고자 행동분석, AChE활성 분석 및 면역조직 화학적 염색을 시행하였다.
재료 및 방법
1. 재료
Scopolamine 유도 기억력 감소 모델의 동물실험은 C57BL/6J 생쥐(수컷, 8 주령, ㈜다물사이언스)를 분양받아 사용하였다. 동물실의 환경은 항온항습(온도 23±2 ℃, 습도 65±2 %) 하에서 12 시간의 명암주기를 유지하였으며 식수는 제한 없이 공급하였다. 실험동물은 1 주간 사육실 에 적응한 후 정상군(N, Normal group), 대조군(C, Control group), 양성대조군(PC, Positive control group), 인삼 투여군(G, Ginseng radix group), 생지황 투여군(R, Rehmanniae radix group), 발효홍삼 투여군(FRG, Fermented-red ginseng group)으로 실험군을 나누었으며, 각 군에 6 마리씩 배정하였다. 본 실험은 우석대학교 실험동물윤리위원회의 승인(WS2019-01)을 받은 후 실험동물을 유지, 관리하고 행동실험 등을 진행하였다.
본 실험에 사용된 인삼(Panax ginseng)과 발효홍삼(Fermented-red ginseng)의 재료인 수삼은 5년근을 금산 수삼시장(금산군, 충남)에서 구입하였고, 생지황(Rehmannia glutinosa)은 ㈜옴니허브 (Daegu, Korea)에서 구입하였다.
2. 방법
인삼 추출물은 건조한 수삼을 증류수에 넣어 5 시간 열수추출한 뒤 여과하였다(pore size: 5μm). 생지황 추출물은 70 %, 80 %, 95 % 농도의 EtOH를 이용하여 총 3일 동안 1일씩 실온에서 침지시켜 3회 반복추출한 후 여과하였다. 발효홍삼은 6 시간 일광 건조한 수삼을 95 ℃에서 3 시간을 증숙한 뒤 Paecilomyces variotii var.brunneolus 배양액속에 넣어 30 ℃에서 48 시간 발효시켰다12). 발효된 수삼은 다시 건조기에 넣고 60 ℃에서 10시간, 그리고 50 ℃에서 10시간을 건조시켜 발효홍삼을 제조하였다. 그리고 증류수에 넣어 80 ℃와 90 ℃에서 각각 8 시간씩 중탕하고 90 ℃에서 8 시간 한번 더 중탕하여 총 3 회 추출한 뒤 여과하였다. 그 후 여과액들은 감압농축한 후에 동결건조하여 분말시료를 얻었으며, 실험 농도에 맞게 생리식염수에 희석하여 사용하였다. 회수한 인삼과 생지황과 발효홍삼의 수율(yield)은 각각 47.7 %, 14.8 %, 47.7 %이었다.
시료 물질은 정상군과 대조군(생리식염수 투여군)의 경우 멸균수를, PC군의 경우 Donepezil 5 mg/kg의 농도로, G군, R군, FRG군의 경우 각 한약재 동결건조물 800 mg/kg의 농도로 경구투여 하였다. 경구투여 30분 후, 기억력 손상을 유발하기 위해 정상군을 제외한 대조군과 시료 물질 투여군인 4군에는 Scopolamine 2 mg/kg의 농도로 복강 투여하여 각각 주 5 회 6 주간 진행하였다.
Y-maze test13)에 사용된 기구의 각 구역은 길이 37 ㎝, 넓이 3 ㎝, 높이 15 ㎝로 120 °의 각도를 이룬 사방이 막힌 흰색의 polyvinyl plastic으로 각각의 가지를 A, B, C로 정한 뒤 시료를 투여하기 직전 및 투여 후 2주, 4주, 6주에 정해진 한 구역에 실험동물을 놓은 후 자유롭게 움직이게 하였고, 영상추적 프로그램 (SMART VIDEO TRACKING software ver. 3.0.05, Panlab, Barcelona, Spain)을 이용하여 5분 동안 행동실험을 분석하였다. 실험동물이 구역에 완전히 들어가거나 갔던 구역에 다시 들어간 경우(number of arm entries)를 기록하였다. ABC, CAB, BCA 3개의 다른 구역에 차례로 들어가는 비율은 자발적 변경 행동률(spontaneous alternation)은 다음의 계산식에 의해 계산하였다.
Morris water maze test14)는 지름 90 ㎝, 높이 60 ㎝인 circular water maze를 사용되었다. 물의 온도는 30±1 ℃로 일정하게 유지되는 물을 채웠다. 내부에는 흰색으로 페인트칠하고, 수조 안은 물과 흰색 식용 색소를 풀어서 platform이 보이지 않게 하여 시각단서를 차단하였다. Morris water maze test는 4 개의 사분원으로 남서(SW), 남동(SE), 북서(NW), 북동(NE)로 구분하였다. Escape platform은 지름 15 ㎝, 높이 30 ㎝의 흰색 원 받침대를 SW 구역에 수면보다 2 ㎝ 낮게 부착하여 위치시켰다.
실험동물은 약물 투여 전 4 차례 남서(SW), 남동(SE), 북서(NW), 북동(NE) 순으로 생쥐를 입수시키고 30 초 동안 platform을 찾아가게 하며 platform에 오른 경우 5 초간 머무르게 하고, 오르지 못하면 10초 간 platform에 머물게 하여 기억훈련을 시행하였다.
약물 투여 후 2 주, 4 주, 6 주에 platform을 제거하고 원형 수조의 남서(SW) 구역에서 시작하여 90 초 동안 수영하면서 platform을 찾게 하는 실험을 진행하여 영상추적 프로그램 (SMART VIDEO TRACKING software ver. 3.0.05, Panlab, Barcelona, Spain)을 통해 분석하였다15,16).
6 주간의 실험을 종료한 후 실험동물을 12 시간 절식시킨 다음, diethyl ether로 마취를 진행하고 흉강을 절개하여 심장을 통하여 생리식염수로 관류 및 방혈한 뒤 AChE 분석을 위해 뇌 조직을 적출하여 PBS로 세척하였고 해마(hippocampus)를 분리하여 분석에 이용하였다.
뇌 조직의 AChE(acetylcholinesterase) 활성 측정은 EZ-Acetylcholinesterase Assay Kit (DG-ACE100, Dogen, Korea)로 측정하였다. AChE 활성을 측정하기 위하여 각 실험군의 해마(hippocampus)를 0.1 M phosphate buffer(pH 7.5)에 혼합하여 homogenizer(T10basic, IKA Works, Inc., German)로 균질하였다. 10,000×g에서 5 분 동안 원심 분리하였으며, 분리된 상층액을 2배 희석하여 효소원으로 사용하였다. 제조회사의 방법에 따라 96 well에 AChE standard curve와 실험 효소원을 각 well에 넣은 후 AChE assay buffe로 총 용량이 50 μl가 되도록 조정하였다. 각각의 well에 reaction mixture를 50 μl 첨가하여 37 ℃, 30 분 반응시킨 후 microplate reader (Molecular Device, VERSAmax, USA)를 이용하여 570 nm의 흡광도를 측정하였다.
면역조직화학적 염색은 VECTASTAIN® ABC kit (Vector lab. Inc., USA)를 이용하여 시행하였다. 뇌 조직 절편을 0.1 M PB(phosphate buffer)로 세척한 후 MeOH와 30 % H2O2를 혼합한 용액으로 10분간 반응시켜 endogenous peroxidase를 제거하였다. 이 후 0.1 M PB용액으로 세척한 뒤 normal goat serum 처리를 통하여 비 특이적인 염색반응을 제거하였다. primary antibody는 β-amyloid (ab2539, Abcam Inc., USA), Tau (ab151559, Abcam Inc., USA), BDNF (ab108319, Abcam Inc., USA)를 각각 1:400, 1:200, 1:150의 농도로 희석하여 조직 절편에 4 ℃, 24 시간을 반응시켰다. 그 후 조직 절편을 0.1 M PB(phosphate buffer)로 세척 후 Hsu17) 등의 방법에 의거하여 secondary antibody인 biotinylated Anti rabbit IgG (1:200, Vector lab. Inc., USA)를 실온에서 30 분을 반응시켰다. 그 후 다시 조직절편을 0.1 M PB로 세척한 뒤 VECTASTAIN® ABC reagent (1:50, Vector lab. Inc., USA)를 30 분간 반응시킨 후 0.1 M PB로 세척하였다. 이 후 tris buffer에 3-3’diaminobenzidine과 3 % H2O2용액을 혼합한 발색제에 10-20 분간 발색하여 통상적인 방법으로 탈수 및 투명화 과정을 진행하여 permount로 봉입 후 광학현미경을 통해 해마(hippocampus) 신경세포 및 신경섬유의 염색 발현 정도를 비교 관찰하였다. 이는 반 정량적 방법(semiquantitative manner) 평가를 통하여 반응이 나타나지 않는 부분은 음성반응(-), 약한 염색성을 보인 경우 경도 양성반응(+), 중등도 염색성을 보인 경우 중등도 양성반응(++), 강한 염색성을 보인 경우 강한 양성반응(+++)으로 기준을 정하여 염색반응을 평가하였다.
4. 통계처리
본 실험 결과는 SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science, version 22.0, SPSS Inc., USA)를 이용하여 통계분석을 시행하였다. 실험 별 평균±표준편차 (Mean±SD)를 표시하고, 각 실험군 내에 차이를 비교하기 위해 일원배치 분산분석 (one-way ANOVA)을 시행하였다. 사후분석은 Duncan's multiple range test (DMRT)를 실시하였다 (p<0.05).
결 과
1. Y-maze test
경구투여 전 총 이동거리는 N군에 비해 모든 군(C, PC, G, R, FRG)에서 증가하는 경향을 나타내었다.
경구투여 4주에는 대조군(C군)에 비하여 모든 실험군에서 통계적으로 유의하게 총 이동 거리가 감소하였다 (p<0.05) (Fig. 1). 경구투여 6주에서도 대조군에 비하여 모든 실험군에서 PC군과 유사하게 총 이동거리가 감소하였다(Fig. 1).
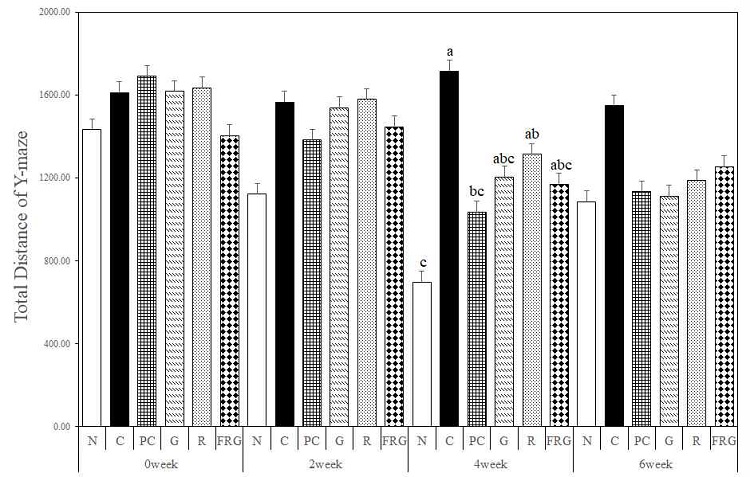
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the total distance for Y-maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b,c) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
경구투여 전 총 입장횟수는 N군이 입장횟수가 가장 증가하였으며 R군이 C군, PC군, G군, FRG군에 비하여 증가하였다. 경구투여 2주에는 대조군에 비해 G군, R군, FRG군의 입장횟수가 크게 증가하였으며, 특히 C군의 총 입장횟수는 가장 많이 감소하였다. 경구투여 4주에는 C군에 비하여 모든 군에서 입장횟수가 증가하였으며, 경구투여 6주에서도 C군에 비하여 모든 군에서 총 입장횟수가 증가하였다 (Fig 2).
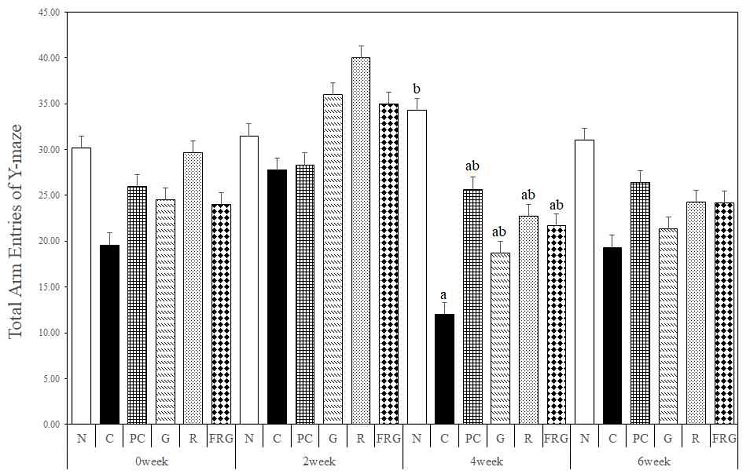
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the total arm entries for Y-maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
경구투여 전 자발적 변경 행동률은 R군에서 가장 낮은 자발적 변경 행동률을 보였지만, 경구투여 2주에서는 모든 군이 유사한 자발적 변경 행동률을 보였다. 경구투여 4주에서는 N군이 크게 증가하여 가장 높은 자발적 변경 행동률을 보였으며 C군은 가장 낮은 자발적 변경 행동률을 보였다. 경구투여 4주의 C군에 비하여 모든 실험군에서 자발적 변경 행동률이 PC군과 유사하게 증가하였다. 경구투여 6주에서는 N군과 C군에서는 유의한 차이를 보였으며(p>0.05), G군, R군, FRG군에서는 C군에 비해 PC군과 유사하게 자발적 변경 행동률이 증가하였다 (Fig. 3).
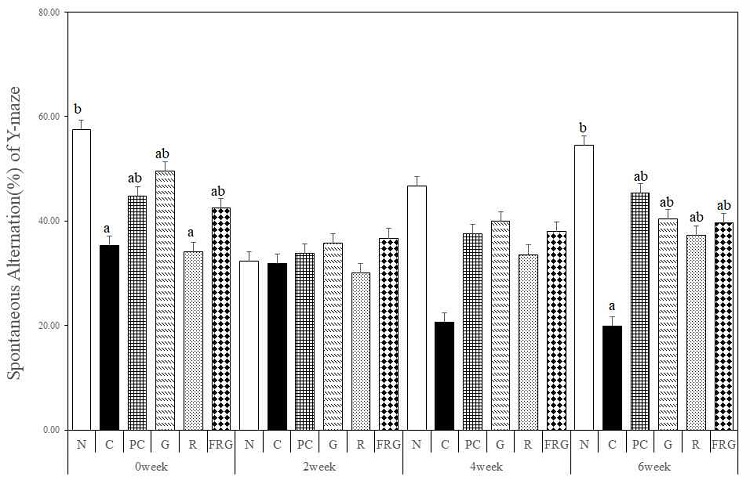
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the spontaneous alternation(%) for Y-maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
2. Morris water maze test
경구투여 전 platform까지 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간은 N군이 C군에 비해 유의하게 감소하였다(p<0.05). 경구투여 2주에서는 C군에 비해 FRG군, G군, R군 및 PC군 순서대로 감소하였다. 경구투여 4주에서는 C군에 비해 FRG군, PC군, R군 순서대로 감소하였으며, G군은 C군보다 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간이 증가하였다. 경구투여 6주에서는 C군에 비해 모든 실험군에서 유사하게 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간이 감소하였다(Fig. 4).
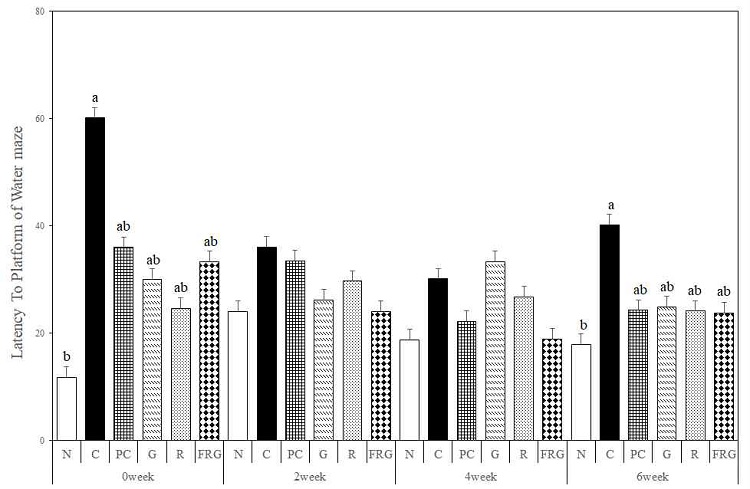
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the latency to platform for Morris water maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
도피대 위에 머무른 시간은 경구투여 전의 C군에 비해 모든 군에서 platform 위치에 머무는 시간이 증가하였다. 경구투여 2주에는 C군에 비해 G군, R군, FRG군에서 머무른 시간이 증가하였으며, 그 중 G군에서 가장 많이 증가하였다. 경구투여 4주에서는 C군에 비해 R군, G군, FRG군, PC군 순서대로 머무른 시간이 증가하였다. 경구투여 6주에서는 C군에 비해 PC군이 가장 오래 도피대위에 머물렀으며, 나머지 모든 실험군에서도 C군에 비해 머무른 시간이 증가하였다(Fig. 5).
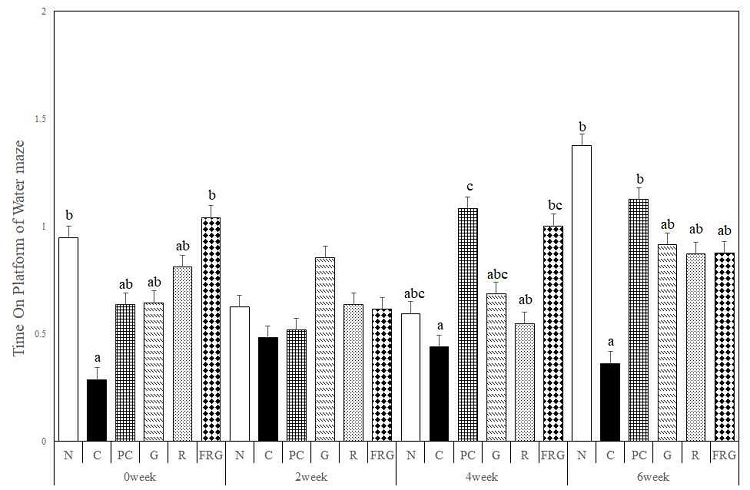
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the time on the platform for Morris water maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b,c) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
도피대 구역에 머무는 시간은 경구투여 전에는 C군에 비해 모든 군에서 오래 머물렀으며, 경구투여 2주에서는 C군에 비해 PC군과 G군에서 오래 머물렀다. 경구투여 4주에서는 C군에 비해 PC군, FRG군, R군이 긴 시간 동안 머물렀다. 경구투여 6주에서는 C군에 비해 모든 군에서 긴 시간동안 머물렀다 (Fig. 6).
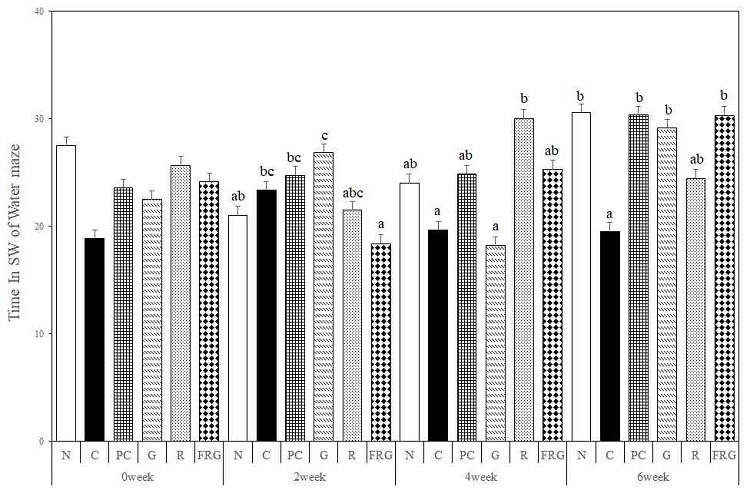
The effects of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented-red ginseng extracts on scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice in the time in SW for Morris water maze test. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Different superscript letter(a,b,c) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
4. 뇌 조직의 AChE 활성
6주간의 실험이 종료된 후 신경세포의 정보전달과 기억과 학습능력과 관련된 acetylcholine의 함량을 확인하기 위하여 실험동물의 해마조직액을 이용하여 acetylcholinesterase(AChE) 활성을 측정하였다. 해마조직내 acetylcholinesterase의 농도는 C군에서는 156.48±10.41 mU/mL로 가장 높았으나 N군, PC군, G군, R군, FRG군은 각각 73.06±7.85 mU/mL, 109.06±1.24 mU/mL, 120.09±8.33 mU/mL, 129.93±3.81 mU/mL, 123.99±4.51 mU/mL로서 C군과 비교하였을 때 통계적으로 유의하게 감소한 것을 확인하여(p>0.05), 결과적으로 AChE 함량의 감소로 인하여 ACh가 증가하여 기억과 학습 능력이 유효하게 개선된 것으로 생각된다(Fig. 7).
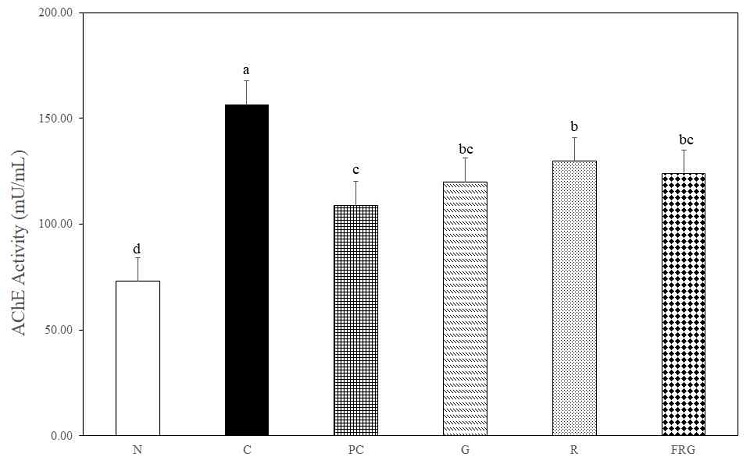
Concentration acetylcholinesterase in hippocampus serum for scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice. N; Normal Group, C; Control Group, PC; Positive control Group, G; Ginseng Group, R; Rehmanniae Group, FRG; Fermented-red ginseng Group. Values are expressed mean ± SD. Different superscript letter(a,b,c,d) mean significantly different between all the experimental groups at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test.
(1) Anti β-amyloid-protein
6 주간의 실험 종료 후 실험동물 뇌 조직의 해마에서 β-amyloid 양성 세포의 면역조직화학적 염색반응은 다음과 같다 (Fig. 8). C군에서는 N군에 비해 PoDG와 DG에 신경섬유가 강한 양성반응(+++)으로 표지되었으며, CA1, CA2 및 CA3에서는 중등도(++)로 표지되었다. PC군에서는 C군에 비해 전반적으로 모든 영역에서 미약한(+) 반응을 나타내었다. 실험군들과 C군간에 비교하면 모든 실험군에서 C군에 비하여 미약한(+) 반응을 나타내었으며, 실험군들에서는 G군이 R군과 FRG군에 비하여 미약한 반응을 나타내었다(Table 1).
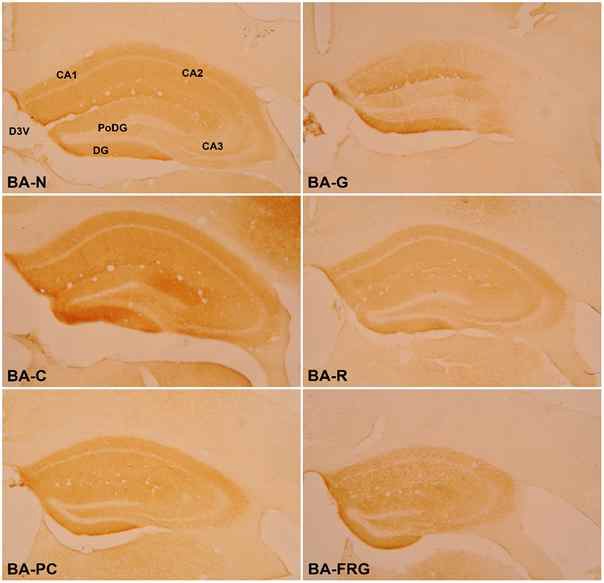
Effect of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented Red ginseng radix extracts on β-amyloid-positive cells in the hippocampus of scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice. BA-N : Normal group, BA-C : Control Group, BA-PC : Donepezil Group, BA-G : Ginseng Group, BA-R : Rehmanniae Group, BA-FRG : Fermented Red Ginseng Group; CA1 : Cornu Ammonis Area 1, CA2 : Cornu Ammonis Area 2, CA3 : Cornu Ammonis Area 3, PoDG : Polymorphic layer of the Dentate Gyrus, DG : Dentate Gyrus, D3V : Dorsal 3rd Ventricle

The change of β-amyloid immunoreactive neurons in hippocampus of scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice
(2) Anti Tau-protein
6 주간의 실험 종료 후 실험동물 뇌 조직의 해마에서 Tau protein 양성 세포의 면역조직화학적 염색반응은 다음과 같다 (Fig. 9). C군에서는 N군에 비해 CA3는 강하고(+++), DG는 중등도(++), CA2는 미약한(+) 양성반응으로 표지되었으며, 이외의 영역에서는 음성반응(-)을 나타내었다. PC군에서는 C군에 비해 DG(-)를 제외한 모든 영역에서 미약한(+) 면역반응을 나타내었다. 실험군들과 C군간에 비교하면 모든 실험군에서 C군에 비하여 CA3와 DG에서 미약한(+) 반응을 나타내었으며, 실험군들에서는 G군이 R군과 FRG군에 비하여 미약한 반응을 나타내었다 (Table 2).
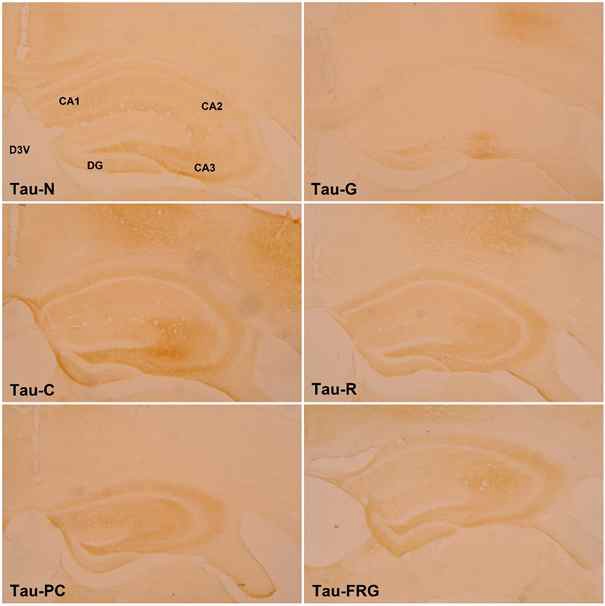
Effect of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented Red ginseng radix extracts on Tau-positive cells in the hippocampus of scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice. Tau-N : Normal group, Tau-C : Control Group, Tau-PC : Donepezil Group, Tau-G : Ginseng Group, Tau-R : Rehmanniae Group, Tau-FRG : Fermented Red Ginseng Group; CA1 : Cornu Ammonis Area 1, CA2 : Cornu Ammonis Area 2, CA3 : Cornu Ammonis Area 3, PoDG : Polymorphic layer of the Dentate Gyrus, DG : Dentate Gyrus
(3) Anti BDNF-protein
6 주간의 실험 종료 후 실험동물 뇌 조직의 해마에서 BDNF 양성 세포의 면역조직화학적 염색반응은 다음과 같다 (Fig. 10). N군에 비해 C군에서는 PoDG와 DG에서 미약한(+) 면역반응을 나타내었다. PC군에서는 PoDG와 DG에서 중등도(++)의 면역반응을 나타내었다. 실험군들과 C군간에 비교하면 모든 실험군에서 C군에 비하여 PoDG와 DG에서 강한 중등도(++)의 반응을 나타내었다 (Table 3).
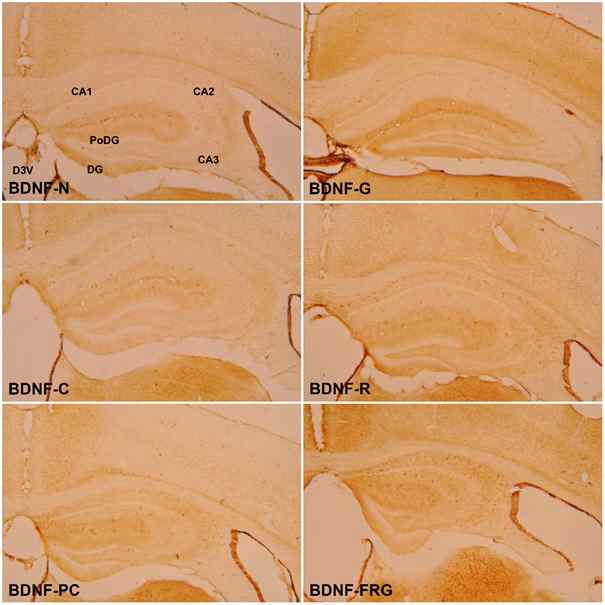
Effect of Ginseng Radix, Rehmanniae Radix and Fermented Red ginseng radix extracts on BDNF-positive cells in the hippocampus of scopolamine-induced memory impaired mice. BDNF-N : Normal group, BDNF-C : Control Group, BDNF-PC : Donepezil Group, BDNF-G : Ginseng Group, BDNF-R : Rehmanniae Group, BDNF-FRG : Fermented Red Ginseng Group; CA1 : Cornu Ammonis Area 1, CA2 : Cornu Ammonis Area 2, CA3 : Cornu Ammonis Area 3, PoDG : Polymorphic layer of the Dentate Gyrus, DG : Dentate Gyrus
고 찰
알츠하이머 질환(Alzheimer's disease, AD)은 기억력과 인지기능이 점진적으로 저하되어 일상생활의 장애를 초래하는 퇴행성 뇌질환이다18). 병리조직학적으로 뇌의 전반적인 위축, 뇌실의 확장, 노인성 반점(Senile plaques) 및 뇌신경섬유종(NFT) 등의 특징을 보이고, 임상적으로는 언어 능력, 판단, 기억 등 지적 기능의 감퇴, 행동 양상, 일상생활능력, 인격장애 등의 증상을 나타내며 격한 행동 인격의 황폐, 우울증세 등의 행동 심리적 증상도 동반될 수 있다19-21). 이로 인한 피해와 부작용을 줄이기 위해서 현재 국내에서는 치매 환자의 기억력 및 인지기능 개선에 효과가 나타나는 천연 약물 또한 기능성 물질에 관한 연구가 요구되고 있는 실정이다.
인삼은 오가과(Araliaceae)의 인삼속(Panax)에 속하는 식물로써 일반적으로 Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer의 말린 뿌리로 면역력 강화, 항 피로, 혈행 개선, 항 스트레스, 항암 활성, 항노화, 우울증 개선 등 많은 효능을 지니고 있다. 이러한 효능은 인삼사포닌인 펩타이드, 산성 다당체, 진세노사이드 등 다양한 생리활성성분을 통해 작용하여 현재에도 활발한 연구가 진행되고 있다22,23).
생지황은 현삼과(Scrophulariaceae)에 속한 다년생 초목으로 지황(Rehmannia glutinosa LIBOSCHITH)의 뿌리이다. 동의보감을 비롯한 한방 서적에 따르면 생지황은 신장과 간 기능의 기능을 도와줄 뿐만 아니라 피를 맑게 하고 타박상으로 인한 염증 제거 등에 효과가 있다고 알려져 있다24).
홍삼은 수삼을 증숙, 건조의 과정을 통하여 제조한 것으로 이러한 수치과정에서 수삼 및 백삼과는 다른 성분이 생성된다고 알려져 있다25). 특징적인 성분으로는 암 예방, 암세포 생장 억제, 항혈전 등의 효과가 있는 prosapogenine(Rg2, RG3, Rh1 및 Rh2) 등의 특이 사포닌으로 사포닌 배당체가 유기산에 의한 산 가수분해 반응을 통해 생성되며, 다양한 비극성 성분 함량이 많은 것으로 알려져 있다26,27).
이에 본 연구에서는 인삼 추출물과 발효공정을 이용하여 기존의 사포닌 성분을 증강시킨 발효홍삼 추출물을 이용하여 인지기능 장애에 대한 효능을 비교하고, 본 교실의 치매모델을 이용한 생지황의 인지개선능에 대한 연구에서 효과를 나타낸 생지황 추출물을 이용하여 scopolamine으로 유도한 기억력 감소모델에서의 기억력 개선 효과를 나타내는지 확인하고자 행동분석, AChE활성 분석 및 면역조직 화학적 염색을 시행하였다.
학습과 기억력 손상을 평가하는 동물실험으로는 Morris water maze test나 fear conditioning test, radial arm maze, noble object recognition test, passive avoidance test, Y-maze test 등이 있다28).
본 연구에서는 Y-maze test와 Morris water maze test를 이용하여 단기 및 장기기억에 대한 공간인지 능력(spatial cognition)을 측정하였다.
Y-maze test 분석 결과 중 총 이동거리의 경우 경구투여 4주는 통계적으로 군 간의 유의성을 보였으며(p<0.05), 대조군을 제외한 모든 군에서 경구투여 후 Y-maze test가 진행됨에 따라 대조군보다 짧은 이동거리를 보였다.
총 이동횟수의 경우 경구투여 4주에 대조군의 총 이동횟수가 현저히 감소하였다. 경구투여 4주의 대조군에 비해 모든 실험군에서 통계적으로 유의성을 보였고(p<0.05), 경구투여 6주에는 대조군에 비해 G군, R군, FRG군 모두 유사하게 총 이동횟수가 증가하였다.
자발적 변경 행동률의 경우 4주부터 대조군과 나머지 다른 군들의 군 간 차이를 보이면서 경구투여 6주에 통계적으로 유의성을 나타냈으며, 대조군에 비하여 G군, R군, FRG군 모두 자발적 변경 행동률이 높은 값을 보였다(p<0.05).
대조군에서는 이동거리는 길었지만, 공간인지 면에서 현저히 떨어지는 것으로 나타났으며, 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼을 경구투여한 군에서 공간인지 능력 개선 효과를 나타낼 가능성을 보여주었다. 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 세 군 모두 PC군과 유사한 값의 자발적 행동률을 나타내어 6주간 투여 시 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 모두 공간인지 능력 개선 효과를 나타내는 것으로 사료된다.
Morris water maze test에서는 platform까지 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간, platform에 머무른 시간, platform이 위치한 남서(SW)구획에 머무른 시간을 분석하였다.
Platform까지 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간은 경구투여 2주와 4주에는 유의성 있는 차이는 없었지만, 경구투여 전에 비하여 경구투여 6주에서 대조군에 비해 유의하게 감소한 PC군과(p<0.05) 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼군이 유사한 값을 보였다.
Platform 위에 머무른 시간의 경우, 경구투여 전과 경구투여를 진행한 주차별 대조군의 결과를 보았을 때 비슷한 시간대를 기록하였다. 경구투여 4주에 PC군과 발효홍삼군의 platform 위에 위치하는 시간이 크게 증가하였으며 마지막 6주째에 정상군이 제일 오래 위치하였고 다음으로 PC군, G군 순이었으며 R군과 FRG군은 매우 비슷한 시간을 기록하였다.
Platform이 위치한 남서(SW)쪽 구획에 머무르는 시간의 경우, 경구투여 2주째에는 인삼군이 가장 긴 시간대를 기록했지만 4주째엔 도피대가 설정되어있던 구획에 위치하는 시간이 감소하였다. 대조군을 제외한 나머지 군들의 시간은 증가하였고 최종 경구투여 6주째에 군 간의 유의한 차이를 보이며(p<0.05) 대조군에 비해 모든 군의 남서(SW)쪽에 위치하는 시간이 증가하며 높은 기록대를 보였다.
Platform까지 찾아가는데 걸리는 시간, platform 위에 머무른 시간의 결과를 종합해보면 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼이 장기적 공간인지 능력의 개선에 있어 효과적이었고 platform이 위치한 남서(SW) 구획에 머무른 시간에 대한 결과를 살펴보면 인삼과 발효홍삼을 투여하였을 때 장기 공간인지능력을 더욱 효과적으로 개선 할 것으로 사료된다.
콜린성 신경세포의 퇴화로 인해 신경전달물질인 ACh의 부족으로 기억 및 인지능력 저하가 일어나며 acetylcholine 분해효소인 AChE의 활성에 의해 ACh 함량이 감소하면서 알츠하이머 병증이 심화되는 것으로 알려져 있다29,30). 이러한 연구 결과를 토대로 AChE의 활성을 측정한 결과 AChE 활성은 N군, PC군, G군, R군, FRG군은 각각 73.06±7.85 mU/mL, 109.06±1.24 mU/mL, 120.09±8.33 mU/mL, 129.93±3.81 mU/mL, 123.99±4.51 mU/mL로써 대조군 156.48±10.41 mU/mL,에 비하여 통계적으로 유의하게 감소한 것으로 나타났다(p>0.05). 이는 대조군에 비해 모든 실험군에서 AChE 활성의 억제 효과를 나타내었으며, acetylcholine(ACh)의 합성 전구체 (ACh precursor) 또는 콜린성 수용체의 효능제(receptor agonist)를 투여하는 방법과 acetylcholinesterase(AChE)의 저해제를 투여하여 시냅스에서의 ACh의 농도를 유지시키는 방법이 저하된 콜린성 신경의 기능을 개선시킨다는 것이 입증되어 치매 치료에 효과적일 것으로 사료된다31).
알츠하이머 질환 발병의 정확한 원인은 밝혀지지 않았지만 뇌세포의 β-amyloid plaques의 축적, Tau-protein의 응집, 산화적 스트레스 및 콜린성 기능 장애(cholinergic dysfunction) 등과 같은 여러 가지 요인들에 의해 발병하는 것으로 알려져 있다32). 또한 CREB의 인산화에 의해서 발현되는 뇌의 신경영양인자(neurotrophic factor)인 BDNF(brain-derived neurotrophic factor)는 신경돌기 성장, 신경회로의 형성과 기억, 학습을 바탕으로 한 신경 시냅스 가소성 조절 등과 관련이 있어 기억력 및 인지능 형성에 중요한 역할을 하며, amyloid 전구체 단백질로부터 amyloidogenic pathway에 의해 분리되어 β-amyloid는 치매의 대표적 조직병리학적 원인으로 알려져 있다32,33). 이에 본 연구에서는 β-amyloid, Tau-protein, BDNF-protein의 분포 정도를 실험동물의 해마에서 반정량적법을 이용하여 비교 관찰하였다.
β-amyloid protein의 염색반응 결과는 대조군이 ‘+’이 12개로 가장 많이 분포되었고, G군의 ‘+’이 4개로 가장 적게 분포되었다. 정상군 및 PC군, R군, FRG군이 5개로 대조군에 비하여 적게 분포되어있는 것을 확인하였다.
Tau-protein의 염색반응 결과는 대조군 ‘+’이 6개로 가장 많이 분포되어있었으며, G군 ‘+’이 1개로 가장 적게 분포되어있었다. 또한, 정상군, R군 및 FRG군, PC군 순으로 ‘+’이 2개, 3개, 4개가 분포하여 대조군보다 적은 발현을 확인하였다.
BDNF-protein의 염색반응 결과는 대조군이 ‘+’이 2개로 가장 적게 분포하였고 가장 많이 분포한 군은 ‘+’이 7개인 FRG군 이었다. 이외, 정상군, PC군, G군, R군 모두 ‘+’이 4개로 대조군에 비하여 많은 발현을 나타내었다.
β-amyloid와 Tau-protein 염색 발현 결과, 가장 효능이 좋은 군은 G군이었으며, BDNF-protein 염색 발현 결과로는 FRG군이 가장 좋은 효능을 나타내었다. R군은 확연하게 좋은 결과는 나타내지 못하였지만 β-amyloid, Tau, BDNF 세 항체 모든 결과에서 대조군보다 좋은 효능을 나타내었다. 이는 대조군에 비하여, G군, FRG군, R군이 뇌 신경세포 손상이 적었음을 의미하고 행동실험 결과와 함께 분석하였을 때 인지장애 치료에 가장 효과가 좋은 것은 인삼과 발효홍삼으로 생각되었다.
이상의 결과를 종합하면 행동분석의 인지기능 개선은 인삼과 발효홍삼이 가장 효과가 있었으며, 기억에 대한 공간인지 능력은 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 모두 효과가 있었다. 기억과 인지능력 저하를 일으키는 AChE 활성은 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 투여 시 AChE의 농도를 감소시켜, ACh의 농도를 유지하여 콜린성 신경 기능을 개선하여 알츠하이머 치매를 지연시킬 것으로 생각되었다. 해마내 β-amyloid와 Tau-protein은 인삼, 생지황 발효홍삼 순으로 낮은 발현을 보였고, BDNF-protein은 발효홍삼, 인삼, 생지황 순으로 높은 발현을 보여 향후 치매 치료 약물로서 긍정적인 영향을 줄 것으로 사료된다.
결 론
본 연구는 scopolamine으로 유도한 기억력 감소 모델 생쥐를 이용하여 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 추출물을 고농도로 6주간 투여하여 기억력과 인지기능의 개선 효과를 관찰하고자 행동분석, AChE 활성 분석 및 면역조직화학 염색을 시행하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
행동분석 결과 중 인지기능 개선은 인삼과 발효홍삼이 가장 효과가 있었으며, 기억에 대한 공간인지 능력은 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 모두 효과가 있었다.
기억과 인지능력 저하를 일으키는 AChE 활성은 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼 투여 시 AChE의 농도를 감소시켜, ACh의 농도를 유지하여 콜린성 신경의 기능을 개선함으로써 알츠하이머 치매의 지연 효과를 관찰하였다.
면역조직 화학적 염색에서는 인삼, 생지황, 발효홍삼이 대조군에 비해 좋은 효과를 나타내었으며, β-amyloid와 Tau-protein은 인삼, 생지황 발효홍삼 순으로 낮은 발현을 보였고, BDNF-protein은 발효홍삼, 인삼, 생지황 순으로 높은 발현을 보였다.
이상의 실험결과로 인삼, 생지황 및 발효홍삼을 투여하였을 때 scopolamine으로 유도한 기억력 감소 모델 생쥐에서 인지장애 예방 및 치료에 대한 가능성을 확인할 수 있었고, 향후 임상시험 활용에 관한 지속적 연구가 진행되어야 할 것으로 사료된다.
References
-
Kim SY. Past and future of drug treatments for Alzheimer's disease. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2018;57(1):30-42.
[https://doi.org/10.4306/jknpa.2018.57.1.30]

-
Kang SJ, Woo JH, Kim AJ. The effects of Korean ginseng on memory loss in a rat models. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2013;42(8):1190-96.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2013.42.8.1190]

-
Kuhl DE, Koeppe RA, Minoshima S, Snyder SE, Ficaro EP, Foster NL, Kilbourn MR. In vivo mapping of cerebral acetylcholinesterase activity in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1999;52(4):691-9.
[https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.52.4.691]

-
Lee JH, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Park SH, Jung CJ, Beik GY, Jung JW. Comparative study on the effects of Korean and Chinese crataegus pinnatifida on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. J Physiol & Pathol Korean Med. 2018;32(6):375-83.
[https://doi.org/10.15188/kjopp.2018.12.32.6.375]

-
Lee MR, Sun BS, Gu LJ, Wang CY, Mo EK, Yang SA, Sung CK. Effects of white ginseng and red ginseng extract on learning performance and acetylcholinesterase activity inhibition. J Ginseng Res. 2008;32(4):341-6.
[https://doi.org/10.5142/JGR.2008.32.4.341]

- Sohn KH, Kim JS. Anti-dementia effects of Cornus officinalis S. et Z. extract on the scopolamine induced dementia in mouse. Kor J Pharmacogn. 2017;48(4):304-13.
- Yoo SK, Kim JM, Park SK, Kang JY, Han HJ, Park HW, Heo HJ. Protective effect of Gabjubaekmok (Diospyros kaki) extract against amyloid beta (Aβ)-induced cognitive impairment in a mouse model. Korean J Food Sci Technol. 2019;51(4):379-92.
- Lee SG, Chai YG, Jung KH, Kim JH. Gene expression profiling of SH -SY5Y cells in neuroprotective effect of total ginsenosides on H202 induced neurotoxicity. J Orient Neuropsychiatry. 2007;18(1):95-110.
- Bae HK, Seo BI. Inhibitory activities of Rehmanniae radix 30% ethanol extract on acute gastritis and peptic ulcers. Kor J Herbol 2019;34(2):1-14.
-
Wang LC, Wang B, Ng SY, Lee TF. Effects of ginseng saponins on β-amyloid-induced amnesia in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103(1):103-8.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.07.010]

-
Yuan QL, Yang CX, Xu P, Gao XQ, Deng L, Chen P, Chen QY. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on transient cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2007;1167:1-12.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.024]

-
Ye L, Zhou CQ, Zhou W, Zhou P, Chen DF, Liu XH, Shi XL, Feng MQ. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside Rd by highly substrate-tolerant Paecilomyces bainier 229-7, Bioresource Technology 2010;101:7871-6.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.102]

-
Sarter M, Bodewitz G, Stephens DN. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist β-carbolines. Psychopharmacology. 1988;94(4):491-5.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212843]

-
Cerejeira J, Lagarto L, Mukaetova-Ladinska E. Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Front Neurol. 2012;3:73.
[https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00073]

-
Ha DC, Ryu GH. Chemical components of red, white and extruded root ginseng. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2005;34(2):247-54.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2005.34.2.247]

- Park HJ, Son CG. Systematic analysis of Ginseng-focused research worldwide. J Korean Oriental Med. 2008;29(1):60-6.
-
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger HX. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981;29(4):577-80.
[https://doi.org/10.1177/29.4.6166661]

-
Cummings J, Lee G, Ritter A, Sabbagh M, Zhong K. Alzheimer,s disease drug development pipeline: 2019. Alzheimer,s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions. 2019;5:272-93.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2019.05.008]

- Yoon JC, Lee SR, Jung IC. The Effects of HyungBangSaBaek-San (JingFangXieBaiSan) on the Alzheimer's disease model induced by βA. J Orient Neuropsychiatry. 2010;21(2):171-89.
- Kim SH. Comparative Study of Ginseng Radix and Rehmanniae Radix extracts on Alzheimer's mouse model(APPswePSEN1dE9) by Behavior and Molecular Factors. Doctoral Thesis. Woosuk University, 2017.
-
Oide T, Kinoshita T, Arima K. Regression stage senile plaques in the natural course of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2006;32(5):539-56.
[https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00767.x]

- Jeong HC, Hong HD, Kim YC, Rho J, Kim KT, Cho CW. The research trend of ginseng processing technology and the status of ginseng industry. Food Science and Industry. 2012;45(4): 59-67.
-
Ha DC, Ryu GH. Chemical components of red, white and extruded root ginseng. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2005;34(2):247-54.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2005.34.2.247]

- Cheon GY. Screening Antioxidants of Rehmannia glutinosa. Master,s Thesis, Mokpo university, 2018.
- Kwak YS, Park JD, Yang JW. Present and its prospect of red ginseng efficacy research. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2003;8(2):30-7.
- Kim HR, Lee CH, Jung MY, Kim JS, Kim HJ, Jeon HS, Lee SH, Kim JH, Shin MJ, Ma SY, Kwon J, Oh CH. Anti-obesity effects of cultivated ginseng, -wild simulated ginseng and-red ginseng extracts. Herbal Formula. Science. 2019;27(4)269-84.
-
Park KH, Kim YS, Jeong JH. Inhibitory effects of ginseng extracts on histamine-release from rat's mast cell. Korean J. Plant Res. 2011;24(1):98-104.
[https://doi.org/10.7732/kjpr.2011.24.1.098]

- Wang SB, Ahn EM, Jung JW. The fruits of Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge ameliorates learning and memory impairments induced by scopolamine. Kor J Herbology. 2009;24(4):165-71.
-
Kee JY, Hong SH, Park JH. Effect of Albizziae cortex water extract on cognition and memory impairments. J Physiol & Pathol Korean Med. 2017;31(5):270-6.
[https://doi.org/10.15188/kjopp.2017.10.31.5.270]

-
Kuhl DE, Koeppe RA, Minoshima S, Snyder SE, Ficaro EP, Foster NL, Kilbourn MR. In vivo mapping of cerebral acetylcholinesterase activity in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1999;52(4):691-9.
[https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.52.4.691]

- Kim YJ. Isolation and Characterization of AChE inhibitory compounds from natural products and their action mechanisms. Seoul National University, 2004.
-
Kim JH, He MT, Kim MJ, Park CH, Lee JY, Shin YS, Cho EJ. Protective effects of combination of carthamus tinctorius L. Seed and Taraxacum coreanum on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci, 2020;28(2):85-94.
[https://doi.org/10.7783/KJMCS.2020.28.2.85]

-
Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science, 1992;256(5054):184-6.
[https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1566067]
