소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스의 항염증 및 항위염 효과
Ⓒ The Society of Pathology in Korean Medicine, The Physiological Society of Korean Medicine
Abstract
Sogunjung-tang (SGJT) is traditional herbal prescriptions used to treat abdominal pain. In this study, we evaluated the effect on inflammation and gastritis through SGJT formulation development. SGJT composition herbal medicine was boiled in water at 95~100℃ for 3 hours and then concentrated. Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM) was prepared using pharmaceutical excipients such as purified water, sodium benzoate, β-cyclodextrin and CMC-Na. Anti-inflammatory experiment was conducted using STM and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in RAW 264.7 cells. Cell survival was measured by MTT method. Nitric oxide (NO) was measured using griess reagents, and pro inflammatory cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and RT-PCR. Also, we verified STM validity in acute gastritis using the ICR mouse. STM was administered oral for three days. And 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol was oral administered 0.5 mL one hour after the last drug administration. Mice were sacrificed 1 hour after 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol administration. The gastric mucosa was visually observed. STM were not toxic in RAW 264.7 cells. Treatment of STM inhibited the production of NO and inflammatory cytokine at the protein and mRNA levels. Also, in the acute gastritis model with the mouse, the treatment of STM improved gastric mucosal bleeding and edema. In summary, it was confirmed that the treatment of STM exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-gastritis effects. Therefore, we suggest that STM may provide a preclinical evidence for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory and gastritis diseases.
Keywords:
Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM), Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-gastritis서 론
염증은 생화학적 반응에서 일어나는 중요한 역할을 하는 인자로 인체에서의 방어 반응으로 작용하게 되며, 감염, 기타 이물질 등의 자극으로 발생하는 과도한 염증 반응으로 neutrohphil과 macrophage와 같은 inflammatory cell들의 과도한 반응으로 inflammatory cytokine들이 염증 반응을 유도하여 염증성 장 질환, 류마티스 관절염, 죽상 동맥 경화증 및 당뇨병 등을 포함한 염증성 질환을 유발하게 된다.1,2) Dexamethasone (Dex)는 염증성 질환, 류마티스 관절염, 알레르기성 질환 및 폐렴 등의 염증치료에 사용되는 약물이다.3,4)
위는 주요 소화기관 중 하나로써, 위염은 가장 흔하게 발병하는 질환으로 4~5% 세계 인구가 한 번 이상은 경험하는 질환이며, 외인성 공격인자 및 내인성 공격인자에 의해서 위 점막의 손상이 일어난다.5-8) 위 점막의 손상은 여러 공격인자들과 위 내부 방어기전이 균형을 이루면서 보호되지만, 공격인자와 방어기전의 불균형이 일어나면 위 점막의 손상으로 위염이 발생되며 한번 생긴 위염은 만성으로 발전하기 쉽다.7,9) 현재 위염치료제로 사용되는 약물은 위산의 분비를 억제하는 H2 receptor antagonist인 cimetidine, ranitidine 및 양성자 펌프억제제 (proton pump inhibitor, PPI) 등이 있지만, 다양한 부작용이 나타나고 있다.10,11) 주요 발병 원인은 위산, 알코올, 스트레스, 불규칙한 식습관, 소염제와 같은 약물의 과다복용, Helicobacter pylori균의 감염 및 NSAID (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug) 등이 있다.12,13) 염산-알코올을 이용한 동물 위염 모델은 직접적인 위벽 손상의 관찰을 통하여 위 점막의 손상정도를 측정할 수 있다.14,15) 알코올의 섭취는 위 점막내 H+-K+-ATP 발현의 촉진으로 free radical의 유도를 통하여 항산화인자인 catalase, glutathione의 생성을 억제하며, reactive oxygen species (ROS)의 형성으로 항산화의 불균형을 일으켜 위 점막의 염증이 발생하게 된다.16,17)
소건중탕 (小建中湯, Sogunjung-tang)은 계지, 감초, 생강, 대추, 작약 및 교이 6가지 한약재로 구성되어진 한약제제로써 중국에서는 Xiaojianzhong-tang로 불리우며 일본에서는 Shokenchu-to로 불려진다.18) 동의보감 (東醫寶鑑)에서 소건중탕은 溫中補虛 和利緩急하며 虛勞, 腹痛 裏急, 咽乾 및 夢遺 등의 증상에 사용되는 것으로 기록되어 있다.19) 또한, 항산화 및 알레르기 효과와 같은 선행연구가 보고되어 있다.20,21) 이와 같이 소건중탕에 대한 다양한 연구가 진행되었으나, LPS로 유도된 대식세포에서의 항염증 및 염산과 에탄올을 이용한 급성 위염 모델에서 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스에 대한 연구가 진행되지 않았다.
이에 본 연구에서는 소건중탕 제형 개발과 함께 RAW 264.7 세포에서 항염증 및 동물실험을 통한 항위염 효능을 알아보고자 하였다. 이에 따라 소건중탕은 항염증 및 항위염 실험을 통하여 유의성 있는 결과를 확인하였기에 보고하는 바이다.
재료 및 방법
1. 재료
본 연구에서 사용된 소건중탕의 구성 한약재 및 용량은 Table 1에 나타내었다. 이 한약재들은 동일약업사 (Deagu, Korea)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. 소건중탕에 사용된 구성 한약재들은 한국한의약진흥원 한의기술R&D2팀 한약재보관실에 보관하였다.
혼합단미연조엑스 제조에 사용된 sodium benzoate, β-cyclodextrin 및 CMC-Na은 ㈜화원약품 (Seoul, Korea)에서 구입하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포의 배양에 사용된 DMEM/high glucose (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin-streptomycin은 Hyclone (Logan. UT, USA)에서 구입하였으며, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), ethanol, chloroform, griess reagent는 Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA)에서 구입하였다. 사이토카인의 검출을 위한 enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit는 R&D system (Minneapolis, MN, USA)에서 구입하였다. RNA 추출 및 DNA 합성 키트는 각각 Takara (Shiga, Japan)에서, cDNA 합성과 PCR에 사용한 모든 시약은 iNtRON (Seongnam, Korea)에서 구입하였다.
동물실험을 위한 hydrochloric acid은 Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. (Osaka. Japan)에서 구입하였다.
소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스의 제조를 위한 구성 약재는 Table 1에 표시하였으며, 약재의 중량 10배에 해당하는 정제수를 넣어 100℃에서 3시간 추출 여과한 후 농축하였다. 농축한 연조엑스는 Table 2의 구성 함량으로 혼합하여 혼합단미연조엑스를 얻었다.
마우스 대식세포주인 RAW 264.7 세포는 한국세포주은행 (KCLB : Seoul, Korea)으로부터 분양받아 사용하였다. 세포배양을 위해 DMEM/high glucose 배지에 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)와 1% penicillin-streptomycin을 첨가하여 사용하였다. 세포는 37℃, 5% CO2 조건에서 배양하였다.
ICR 마우스 6주령 수컷 30마리를 중앙실험동물에서 구입하여 한국한의약진흥원 동물실험실 환경에 1주일 동안 적응시킨 후 실험에 사용하였다. 동물 사육조건은 conventional system으로 온도 23±2℃, 습도 50±5%, 명암주기 (light : dark cycle)는 12시간 주기로 조절하였다. 고형사료와 물을 충분히 공급하였다.
2. 방법
효능평가를 위해 50% DMSO에 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스를 100 ㎎/mL의 농도로 제조한 다음 0.2 μm membrane 여과 후 시료로 사용하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포에서 항염증 실험을 진행하기 위해 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (50, 100 및 200 ㎍/mL)를 LPS처리 1시간 전에 전처리하였으며, LPS (500 ng/mL)는 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 처리 1시간 후 처리하여 6 그리고 24시간 배양하여 실험을 진행하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포에 대한 시료의 처리 농도를 결정하기 위해 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl–2H- tetrazolium bromide (MTT) 용액으로 분석을 실시하였다. RAW 264.7 세포를 96 well plate에 1×104 cells/well로 분주하고, 소건중탕을 농도별(0, 10, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL)로 처리한 다음 37℃, 5% CO2 incubator에서 24시간 배양하였다. 그 후 MTT reagent를 20 μL씩 첨가하여 4시간 동안 반응시킨 후 MTT reagent와 세포 내 탈수소효소의 반응으로 생성된 formazan을 DMSO로 용출한 뒤 microplate reader(Tecan sunrise)를 이용하여 540 nm에서 흡 광도를 측정하였다. 대조군은 시료를 처리하지 않은 배양액으로 세포 생존율은 다음과 같이 계산하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포들을 DMEM/high glucose배지에서 2×105 cell/mL의 밀도로 현탁하였고, 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (50, 100 및 200 ㎍/mL)을 처리하였다. LPS (500 ng/mL)를 처리하여 24시간 뒤에 세포의 상층액을 획득하여 96 well plate에 loading한 다음 griess reagent로 반응한 후 570 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 하였다. NO의 생성량은 백분율로 표기하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포들을 DMEM/high glucose배지에서 2×105 cell/mL의 밀도로 현탁하여 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (50, 100 및 200 ㎍/mL)를 1시간 전처리한 후, LPS (500 ng/mL)를 처리하여 24시간 배양하였다. 전염증성 사이토카인을 측정하기 위해 세포배양액을 취하여 ELISA법으로 정량하였고 이를 백분율로 표기하였다.
RAW 264.7 세포들을 DMEM/high glucose배지에서 2×105 cell/ml의 밀도로 현탁하여 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (50, 100 및 200 ㎍/mL)를 1시간 전처리하였다. LPS (500 ng/mL)를 6시간 처리한 뒤 RNA iso reagent 500 μL를 이용하여 세포를 포집하였고, chloroform 200 μL를 더하여 잘 썩어준 뒤 15,000 rpm에서 15분간 원심분리하여 상층액을 취하였다. 분리한 상층액에 isopropanol을 1:1 비율로 섞은 후 10분간 상온보관 후 15,000 rpm에서 10분간 원심 분리하여 상층액을 버리고 남은 침전물을 80% ethanol로 2회 씻은 후 침전물을 건조시켰다. 그리고 침전물에 DEPC water를 15 μL씩 넣어 total RNA를 용해시켜 정량하였다. Total RNA는 Maxime RT premix kit (iNtRON, Seongnam, Korea)를 이용하여 cDNA를 합성하였다. 유전자 증폭은 특정 primer를 넣고 각 primer에 따른 PCR 조건에 따라 실시하였다. 각 DNA 1.5% agarose gel을 전기영동시켜 UV 검출기로 확인하였다.
ICR 마우스는 3그룹으로 나누어 군당 6마리씩 나누어 실험을 진행하였다. 위 점막의 손상을 유발하기 위해 24시간 전부터 절식시킨 후, 실험 전 정상군과 위 점막 손상 대조군은 증류수를 경구투여하였으며, 약물 치료군은 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (400 ㎎/㎏ : 1회 복용량)을 3일간 경구투여하였다. 마지막 약물 투여 1시간 후 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol을 0.5 mL 씩 경구투여하여 위 점막의 손상을 유발하였다. 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol 투여 1시간 후 개복하여 위 조직을 적출하였다.
급성위염의 위 병변의 영역을 측정하기 위해 내부 표변을 촬영 후 Image J program(Wayne Rasband, National Institutes of Health, Bethesada, MD, USA)를 이용하여 위 병변의 면적(%)을 측정하였다. 위 손상 억제율은 다음과 같이 계산하였다 : Inhibition ratio (%) = {(control lesion area – sample lesion area)/control lesion area} × 100.22) 조직병리학적 분석을 위해 4% formaldehyde 용액으로 고정한 다음 조직의 절편을 4㎛ 두께로 하여 hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)염색을 시행하여 현미경으로 조직의 손상이나 변화를 확인하였다.
모든 실험 결과는 3회 이상 실시하여 그 평균값을 기초로 Mean±S.D.로 나타내었다. 실험결과에 대한 통계처리는 SPSS 분석프로그램으로 one way ANOVA test를 실시한 후 Turkey test로 사후 검증하였다. p-value가 0.05 미만일 경우 유의한 것으로 판정하였다.
결 과
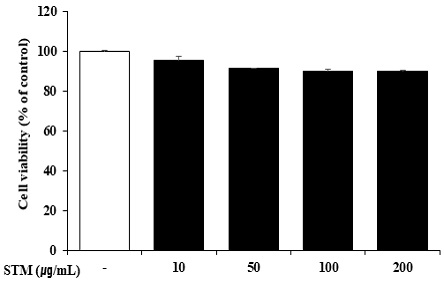
1. 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)가 RAW 264.7 세포에 대한 독성 억제효과
RAW 264.7 세포에서 STM을 전처리하였을 때, 세포 독성에 미치는 영향을 조사하기 위해 STM을 10-200 ㎍/mL 24시간 처리하여 MTT 방법을 이용하여 세포의 생존율을 측정하였다. 그 결과 STM의 200 ㎍/mL 농도까지 세포 독성을 보이지 않았다. 이에 본 연구에 STM의 농도를 200 ㎍/mL까지 최고농도로 설정하여 사용하였다.
2. 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)가 NO 생성 억제 효과
STM의 항염증 효과를 확인하기 위해 염증 매개물질인 NO의 생성에 미치는 영향을 확인하였다. RAW 264.7 세포에 STM을 1시간 전처리 한 후, LPS로 24시간 동안 자극하여 griess 반응으로 NO의 생성을 측정하였다. 그 결과 NO의 생성은 LPS의 자극으로 증가하였고, LPS에 의해 증가된 NO의 생성은 STM의 농도의존적으로 억제하는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 2). Dex와 STM의 NO의 생성 억제를 비교하였을 때, STM 200 ㎍/mL에서 Dex와 비슷한 수준의 NO 생성 억제 효과를 보여주었다.
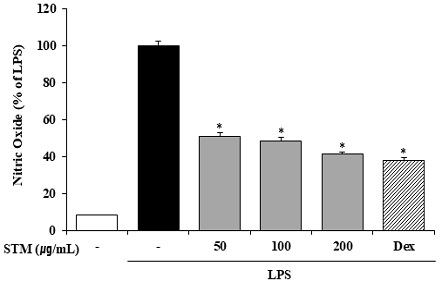
Effects of Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM) on NO Production in RAW 264.7 Cells. STM (50, 100 and 200 ㎍/mL) was pretreated for 1 hour and then incubated with LPS (500 ng/mL) for 24 hours. NO was measured. Similar results were obtained in three experiments. *P < 0.05 vs LPS treatment alone. “Dex” is “dexamethasone”.
3. 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)의 전염증성 사이토카인의 생성 억제효과
RAW 264.7 세포에서 STM을 처리하였을 때 전염증성 매개물질에 미치는 영향을 조사하기 위해 IL-1β, IL-6 및 TNF-α와 같은 염증성 사이토카인을 생성을 확인하였다. STM을 1시간 전처리한 후 LPS를 24시간 동안 자극하여 전염증성 사이토카인의 생성에 미치는 영향을 확인하였다. LPS의 자극은 전염증성 사이토카인의 생성을 유도하였고, STM에 의해 전염증성 사이토카인의 생성이 억제되는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3). Dex와 STM을 비교하였을 때, IL-1β은 Dex와 비슷한 수준으로 억제하는 것을 보여주었으며, IL-6와 TNF-α는 Dex를 처리하였을 때 STM보다 유의적으로 더 억제하였다.
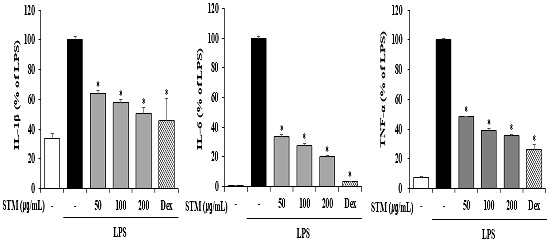
Effect of Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM) on Pro-inflammatory Cytokine Production in RAW 264.7 Cells. STM (50, 100 and 200 ㎍/mL) was pretreated for 1 hour and then incubated with LPS (500 ng/mL) for 24 hours. Pro inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) were measured by ELISA. Similar results were obtained in three experiments. *P < 0.05 vs LPS treatment alone. “Dex” is “dexamethasone”.
4. 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)의 mRNA 수준에서의 전염증성 사이토카인 발현 억제효과
RAW 264.7 세포에서 STM을 전처리하였을 때, 단백질 수준에서 IL-1β, IL-6 및 TNF-α와 같은 전염증성 사이토카인의 증가를 억제하는 것을 확인하여, mRNA 수준에서 또한 전염증성 사이토카인의 발현이 억제되는지 확인하였다. STM을 1시간 전처리한 후 LPS를 6시간 동안 자극하여 전염증성 사이토카인의 발현을 확인하였다. LPS의 자극은 mRNA 수준의 전염증성 사이토카인을 증가시켰으며, STM의 전처리는 전염증성사이토카인의 발현을 억제시키는 것으로 확인하였다(Fig. 4). Dex와 STM을 비교하였을 때, Dex가 IL-1β, IL-6 및 TNF-α를 더 유의적으로 억제하였다.
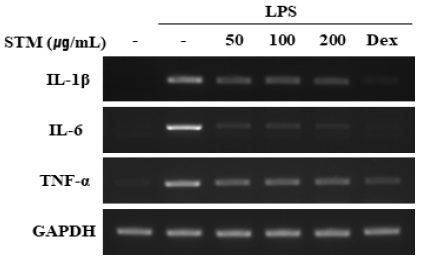
Effects of Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM) on the production of inflammatory cytokines at mRNA level in RAW 264.7 cells. STM was pre-treated in RAW 264.7 cells for 1 hour, and then incubated with LPS for 6 hours. The mRNA levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were determined by RT-PCR. Similar results were obtained in three experiments.
5. 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)의 위점막 손상 개선 효과
150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol으로 유도한 위염의 위 점막에서 출혈이나 부종으로 인하여 위 점막 손상이 나타났고, STM을 투여하였을 때 유의적으로 위 점막의 손상이 개선됨을 확인하였다(Fig. 5A). 또한. 조직병리학적 검사에서 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol으로 유도한 그룹에서 출혈 및 위상피세포간의 경계가 허물어진 것을 확인하였으며, STM을 처리하였을 때 개선되었다(Fig. 5B). 다음으로 위 병변을 확인하였으며 STM을 처리한 그룹에서는 위 손상 억제율은 43.8%로 유의적인 위 손상 억제효과를 나타내었다(Fig. 5C).
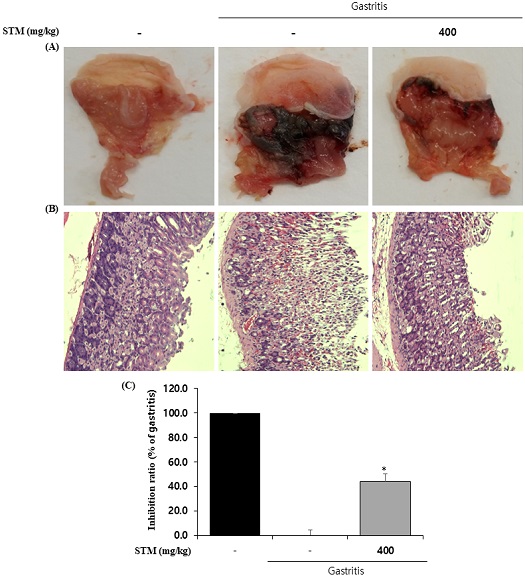
Effect of Sogunjung-tang mix soft extract (STM) on 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol-induced gastritis. After pre treatment of STM (400 ㎎/㎏, oral) for 3 days, 0.5 mL of 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol was injected 1 hour later. It was sacrificed 1 hour after 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol oral administration. (A) Representative photographs of 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol-induced gastritis. (B) Hematoxylin & eosin (H&E)-stained of histological sections of gastric mucosa in gastritis. (C) Inhibition ratio(%) of gastric mucosal damage in gastritis. Similar results were obtained in three experiments.
고 찰
소건중탕은 임상에서 中氣虛寒하며 陰陽氣血이 失調하여 발생하는 질환에 사용되는 처방으로 일본에서는 경련성 복통, 교이를 제거한 소건중탕은 경련성 변비, 허약체질 아동의 체질개선 등에 사용한다고 알려져 있다.23) 한약제제는 예로부터 오랜 임상에서 사용한 경험을 토대로 다양한 질환 분야에서 치료 목적으로 사용되어 왔다. 하지만 한약재를 물에 끓인 후 제조하는 탕약은 약재의 쓴맛, 안정성, 유효성 및 복용의 순응도가 떨어지는 단점을 가지고 있어 기존의 한약탕제와는 다른 산제, 정제, 연조엑스 등 현대적인 제형개발 등 한약제제의 활성화를 위한 많은 연구들이 진행되고 있다.24,25)
본 연구에서는 소건중탕의 제형 개발 및 LPS로 유도한 염증에 대한 항염증 및 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol으로 유도한 급성 위염에 대한 항위염 효과를 확인하고자 하였다.
염증은 인체에서 물리적 작용이나 화학적 물질, 세균 감염 등의 침투로 손상부위를 재생하려는 기전으로 지속적으로 또는 과도한 염증반응은 다양한 염증성 질환의 원인이 된다.26) 대식세포는 선천성 면역반응으로 병원균 감염 초기에 중요한 역할을 담당하며, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), cytokine 등의 자극을 받으면 활성화되어 interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 및 tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α 와 같은 염증성 사이토카인 및 염증매개물질인 NO를 생성한다.27,28) 따라서 본 연구에서 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스의 염증에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위해 마우스 대식세포인 RAW 264.7 세포에서 항염증 효과를 확인하였으며, 또한, 위염에 대한 효과를 확인하기 위해 마우스에서 항위염 효과를 확인하였다. NO는 NO synthase (NOS)에 의해 L-arginine으로부터 생성되며, LPS의 자극은 iNOS의 활성으로 과량의 NO를 생성하면서 면역 및 염증 반응에 관여한다고 보고되어 있다.29,30) 또한, 염증의 지표인 IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α와 같은 전 염증성 사이토카인은 다양한 염증매개체를 유도하거나 면역반응을 조절하는데 있어 중요한 역할을 한다.31) 본 연구에서는 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스는 세포의 독성이 보이지 않았으며, 염증 매개체인 NO의 생성 및 전 염증 사이토카인의 분비를 억제를 통해 항염증에 대한 유의적인 효과를 보여주었다.
위염은 상복부 중앙에서 통증으로 메스꺼움, 구토 및 체중감소와 같은 증상이 일어나며, 위산, 알코올, 비스테로이드성 약물, 산화적 스트레스 및 각종 약물 등 유해인자들에 의해 불균형을 이루며 염증, 출혈 및 발적이 나타나는 형태의 질환이다.32-34) 본 연구에서는 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol으로 유도된 급성위염모델을 이용하였다. HCl은 위를 자극하여 위 운동의 증가로 위 손상을 더욱 악화시키며, ethanol은 위 점막의 자극으로 출혈과 손상을 일으키는 것으로 알려져 있다.34) 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스를 3일간 전처리한 후 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol을 처리하고 부검을 통하여 위 조직을 육안으로 관찰한 결과, 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스의 전처리로 위 점막의 출혈 및 부종이 유의하게 억제되었다.
이상 소건중탕을 보관 및 복용의 편의성이 높은 연조엑스제로 제형 개발하여 염증 및 위염에 대한 효능을 확인하였다. 결론적으로, 소건중탕의 항염증 및 항위염에 대한 효과는 염증성 질환에 있어서 예방 및 치료에 사용할 수 있는 기초적인 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
결 론
본 연구는 소건중탕의 보관 및 복용의 편의성이 좋은 혼합단미연조엑스 제형으로 개발하였으며, 효능 평가를 통해 다음과 같은 결과를 얻었다.
소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)는 농도의존적으로 NO의 생성을 억제하였다.
소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)는 단백질 및 mRNA 수준에서 IL-1β, IL-6 및 TNF-α와 같은 사이토카인을 억제하였다.
소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)는 150 mM HCl in 60% ethanol로 유도한 위 점막내 손상으로 인한 출혈과 부종을 개선하였다.
이상의 결과로 소건중탕 혼합단미연조엑스 (STM)은 항염증 및 항위염에 대한 효과가 있을 것으로 사료된다.
References
-
Behrens EM. Macrophage activation syndrome in rheumatic disease: What is the role of the antigen presenting cell? Autoimmun Rev. 2008;7(4):305-8.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.025]

-
Lopez-Bojorquez LN, Dehesa AZ, Reyes-Teran G. Molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of septic shock. Arch Med Res. 2004;35(6):465-79.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2004.07.006]

-
Tian Y, Zhou S, Takeda R et al. Anti-inflammatory activities of amber extract in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2021;141:111854.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111854]

-
Baek JY, Kang KS, Lee AY. Anti-inflammatory Property of Chicken Feet, Acanthopanax, and Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Mixture Extract in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. KSBB Journal. 2020;35(4);330-6.
[https://doi.org/10.7841/ksbbj.2020.35.4.330]

- Banks WJ. Applied veterinary histology, 2nd ed, William & Wilkins Baltimore. 1986:393-6.
-
Kim SH, Lee JA, Lee RA, et al. Protective Effect of Gardenia Fruit Ethanol Extract in HCl/Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastritis. J Kor Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2019;48(2):198-205.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2019.48.2.198]

- Kim MH, Lee HS, Lee HA, et al. Effect of Lentinus edodes extract against acute gastritis in Wistar Rats. J Animal Assisted Psychotherapy. 2017;6(2):79-84.
- Lee JA, Kim SH, Kim MJ, et al. Protective Effects of Chrysanthemi Indici Flos Extract and Flaxseed Oil Mixture on HCl/ethanol-induced Acute Gastric Lesion Mice. Kor. J. Herbol. 2018;33(6):19-28.
-
Lee JY, Kwon OJ, Noh JS, et al. Protective effects of red ginseng according to steaming time on HCl/ethanol-induced acute gastritis. J Appl Biol Chem. 2016;59(4):365-72.
[https://doi.org/10.3839/jabc.2016.062]

-
Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Proton pump inhibitors, histamine H2 receptor antagonists, and other antacid medications and the risk of fracture. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;79(2):76-83
[https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0021-7]

-
Haga Y, Nakatsura T, Shibata Y, et al. Human gastric carcinoid detected during long-term antiulcer therapy of H2 receptor antagonist and proton pump inhibitor. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43(2):253-7.
[https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018881617038]

-
Kim OK, Nam DE, You YH, et al. Protective Effect of Canavalia gladiata on Gastric Inflammation Induced by Alcohol Treatment in Rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2013;42(5):690-6.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2013.42.5.690]

-
Lee JJ, Choi HS, Lee JH, et al. The Effects of Ethylacetate Fraction of Sanguisorba officinalis L. on Experimentally-induced Acute Gastritis and Peptic Ulcers in Rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2005;34(10):1545-52.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2005.34.10.1545]

-
Anandan R, Rekha RD, Saravanan N, et al. Protective effects of Picrorrhiza kurroa against HCl/ethanol-induced ulceration in rats. Fitoterapia. 1990;70(5):498-501.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-326X(99)00081-7]

-
Zheng YF, Xie JH, Xu YF, et al. Gastroprotective effect and mechanism of patchouli alcohol against ethanol, indomethacin and stress-induced ulcer in rats. Chem Biol Interact 2014;222:27-36.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2014.08.008]

-
del Valle JC, Salvatella M, Rossi I, et al. Impairment of H+-K+-ATPase-dependent proton transport and inhibition of gastric acid secretion by ethanol. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280(6):G1331-40.
[https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.2001.280.6.G1331]

-
Kim MY, Kwon OJ, Noh JS, et al. Inhibitory Activities of Water Extracts of Black Ginseng on HCl/Ethanol Induced Acute Gastritis through AntiOxidant Effect. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2016;45(9):1249-56.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2016.45.9.1249]

-
Seo CS, Shin HK. Phytochemical analysis of twelve marker analytes in Sogunjung-tang using a high-performance liquid chromatography method. Applied Sciences. 2020;10(23):8561.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238561]

-
Lee DE, Jang HY, Lee YL, et al. Clinical Study of Sogunjung-tang Granules in 30 Cases of Heartburm. The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine. 2019;40(6):1193-1201.
[https://doi.org/10.22246/jikm.2019.40.6.1193]

- Park SY, Baek JH, Seo JM. Effect of Gamisogunjung-tang on Antioxidation Activity in Rats Induced Aging by D-Galactose. J Korean Oriental Pediatrics 2005:19(1):153-71.
- Jung IH, Kim JY, Kam CW, et al. Inhibitory Effects on the Type I hypersensitivity and Inflammatory Reaction of Sogunjung-tang. Journal of physiology & pathology in Korean Medicine 2003:17(5):1188-93.
-
Kwon DA, Kim YS, Baek SH. Protective effects of a standardized extract (HemoHIM) using indomethacin- and ethanol/HCl-induced gastric mucosal injury models. PHARMACEUTICAL BIOLOGY. 2019;57(1):543-9.
[https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2019.1651875]

-
Lee DE, Jang HY, Lee YL, et al. Clinical Study of Sogunjung-tang Granules in 30 Cases of Heartbur. J. Int. Korean Med. 2019;40(6):1193-1201.
[https://doi.org/10.22246/jikm.2019.40.6.1193]

-
Choi HM, Kim SJ, Kim IS, et al. Evaluation on Anti-oxidant Activity and Anti-inflammatory Effects for the New Formulation of Gamisoyosan. Kor. J. Herbol. 2016;31(6):1-9
[https://doi.org/10.6116/kjh.2016.31.6.1.]

- Han K, Kwon DY, Lee SG, et al. The present state of korean herbal preparation production and possible improvement plan. Korean J. Oriental Med. Prescrip. 2006;14(1):30-41.
- Cheon MS, Yoon TS, Choi GY, et al. Comparative Study of Extracts from Rhubarb on Inflammatory Activity in Raw 264.7 Cells. Korean Journal of Medicinal Crop Science. 2009;17(2):109-14.
-
McDaniel ML, Kwon G, Hill JR, et al. Cytokines and nitric oxide in islet inflammation and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996;211(1):24-32.
[https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-211-43950D]

- Kim DH, Park SJ, Jung JY, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of the aqueous extract of Hwangnyenhaedok-tang in LPS-activated macrophage cells. Kor J Herbol. 2009;24(4):39-47.
-
Ajizian SJ, English BK, Meals EA. Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(4):939-44.
[https://doi.org/10.1086/314659]

- Guzik T, Korbut R, Admek-Guzik T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003;54(4):469-87.
-
Kim MJ, Bae GS, Choi SB, et al. The anti-inflammatory effect of Taraxacum coreanum on lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response on RAW 264.7 cells. Kor. J. Herbology. 2014;29(6):21-6.
[https://doi.org/10.6116/kjh.2014.29.6.21.]

-
Lee AR, Lee JY, Kim MY, et al. Protective Effects of a Lycium chinense Ethanol Extract through Anti-oxidative Stress on Acute gastric lesion mice. Kor. J. Herbol. 2015;30(6):63-8.
[https://doi.org/10.6116/kjh.2015.30.6.63.]

-
Kim MY, Kwon OJ, Noh JS, et al. Inhibitory Activities of Water Extracts of Black Ginseng on HCl/Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastritis through AntiOxidant Effect. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2016;45(9):1249-56.
[https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2016.45.9.1249]

- Lee JA, Kim SH, Kim MJ, et al. Protective Effects of Chrysanthemi Indici Flos Extract and Flaxseed Oil Mixture on HCl/ethanol-induced Acute Gastric Lesion Mice. Kor. J. Herbol. 2018;33(6):19-28.