심박변이도를 활용한 한의학 진단의 객관화: 현황에 대한 주제범위 문헌고찰
Ⓒ The Society of Pathology in Korean Medicine, The Physiological Society of Korean Medicine
Abstract
This scoping review aimed to examine the current status of research utilizing heart rate variability (HRV) for diagnosis in Korean Medicine (KM) and traditional East Asian medicine, and to explore its potential for objectifying KM diagnostic methods. A systematic search was conducted in Medline and Embase databases. Studies published in English that used HRV for diagnostic purposes in KM or traditional East Asian medicine were included. Data extraction and analysis were performed according to predefined criteria. Fifteen studies met the inclusion criteria. The research designs were categorized into five types: TEAM Pattern and Symptom Analysis, Comparative Analysis, Diagnostic Tool Development, HRV Pattern Development for Specific Conditions, and Physiological Indicator Correlation Analysis. The studies revealed significant relationships between HRV parameters and various concepts in traditional East Asian medicine, including constitution types, symptoms, and pattern identifications. Several studies demonstrated the potential of HRV in objectifying and modernizing traditional diagnostic methods. This review suggests that HRV analysis has significant potential as a tool for objectifying KM diagnosis. It can provide a bridge between traditional medical theories and modern physiological measurements. Further research is needed to standardize HRV measurement protocols in KM and to develop more robust diagnostic tools based on HRV analysis.
Keywords:
Heart rate variability, Korean medicine, Traditional East Asian medicine, Diagnosis, Scoping review서 론
한의학 및 동아시아 전통의학은 수천 년의 역사를 통해 축적된 지식과 경험을 바탕으로 독특한 진단 및 치료 체계를 발전시켜 왔다. 그러나 현대 의학의 과학적 패러다임이 강조되면서, 이러한 전통 의학 체계의 진단 방법에 대한 객관성과 재현성 문제가 지속적으로 제기되어 왔다1,2). 특히, 한의학의 사진(四診) 체계인 망문문절(望聞問切)은 의사의 주관적 경험과 판단에 크게 의존하며, 이는 진단의 일관성과 표준화에 어려움을 초래한다. 이러한 한계는 한의학 진단의 과학적 검증과 현대 의료 체계로의 통합을 방해하는 주요 요인으로 작용해 왔다.
이러한 배경에서, 생체신호 기반 진단 방법의 도입은 전통의학 진단의 객관화와 표준화를 위한 유망한 접근법으로 주목받고 있다. 현대 의학 분야에서는 이미 다양한 생체신호를 활용한 진단 기술이 개발되어 임상에서 활용되고 있다. 예를 들어, 심전도(ECG)를 이용한 심장 질환 진단3), 뇌전도(EEG)를 통한 신경학적 이상 탐지4), 그리고 근전도(EMG)를 활용한 근육 질환 평가5) 등이 그 대표적인 사례이다. 이러한 생체신호 기반 진단 방법들은 높은 객관성과 재현성을 제공하며, 임상적 의사결정을 지원하는 데 중요한 역할을 하고 있다.
한편, 생체신호 중 심박변이도(Heart Rate Variability, HRV)는 자율신경계 기능을 비침습적으로 평가할 수 있는 유용한 도구로 주목받고 있다. 심박변이도는 연속된 심박 간 간격의 변화를 측정하는 방법으로, 교감신경계와 부교감신경계의 균형 및 전반적인 자율신경계 기능을 반영한다6). 심박변이도를 이용한 진단 관련 연구는 현대 의학 분야뿐만 아니라 한의학 영역에서도 활발히 진행되고 있다. 예를 들어, 박 등이 만성변비환자에서 심박변이도 지표와 한열 변증 간의 연관성을 연구하였으며7), 이 등은 다한증 환자에서 심박변이도 지표를 바탕으로 한의학적 변증 특성과 자율신경 기능과의 상관관계를 탐구하였다8). 또한 2012년에 국내에 발표된 심박변이도 검사를 활용한 논문에 대한 고찰 연구9)는 수행된 바 있으나 보다 범위를 넓혀 국제적으로 동아시아 전통의학의 진단과 관련하여 심박변이도의 활용에 대한 고찰 연구는 수행된 바 없다.
본 연구에서는 심박변이도를 활용한 한의학 진단 연구의 동향과 특성을 포괄적으로 파악하기 위해 주제범위 문헌고찰 방법을 선택하였다. 주제범위 연구는 아직 체계적 문헌고찰이 이루어지기 어려운 신흥 연구 분야나 이질적인 연구들로 이루어진 분야의 연구 경향을 조사하는 데 적합한 방법론이다10). 심박변이도 기반 한의 진단 연구는 아직 초기 단계로 연구 설계와 방법론이 다양하므로, 이를 아우르는 탐색적 접근으로서 주제범위 연구가 적절하다고 판단하였다. 이러한 배경에서, 본 연구는 심박변이도를 활용한 한의학 및 동아시아 전통의학 진단 관련 연구의 현황을 파악하고, 이를 통해 심박변이도의 한의학적 진단에의 활용 가능성을 탐색하고, 추후 심박변이도 기반의 객관적 진단 도구 개발을 위한 기초 자료를 제공하고자 한다.
연구대상 및 방법
1. 연구설계, 연구질문 설정 및 문헌 검색
본 연구는 심박변이도를 활용한 한의학 및 동아시아 의학의 진단 관련 연구동향을 파악하기 위한 주제범위 문헌고찰 연구이다. 주요 연구 질문은 심박변이도를 한의학 진단에 대한 판단의 근거로 활용한 연구를 찾는 것이었다. 문헌고찰 계획(protocol)은 공식기관에 등록하지는 못했으나, 문헌 검토를 시작하기 전에 계획을 세워 이에 따라 연구를 진행하였다. 문헌 검색은 주제범위 연구를 위한 체계적 문헌고찰 및 메타분석 보고 지침(PRISMA-ScR)에 따라 수행되었다11).
주제범위 문헌고찰의 초점을 명확하게 하고 효과적인 검색 전략을 수립하기 위한 연구질문을 설정하기 위해 핵심요소를 구성하였다10). 목표 인구집단(population)은 열려있고, 개념(concept)은 심박변이도 검사, 맥락(context)은 한의학을 포함한 동아시아 전통의학이며, 관심 결과(outcomes)는 심박변이도의 한의 진단에의 활용가능성으로 하였다. 따라서 본 연구 질문은 ‘한의학을 포함한 동아시아 전통의학에서 진단 과정에 심박변이도를 활용하기 위하여 어떤 연구들이 이루어졌는가’이다.
데이터베이스 검색은 Pubmed를 통한 Medline과 Embase에서 “동아시아 전통의학”과 “심박변이도”를 영어로 조합한 검색 쿼리를 사용하여 수행하였으며 2024년 6월 30일을 최종 검색 기준일로 하였다(Table 1).
2. 문헌 선정 기준 및 문헌 선정
검색한 자료 중 영어로 작성된 원고만을 대상으로 하였다. 심박변이도 검사가 수행된 연구를 포함하였다. 원본 연구만을 포함하였으며, 리뷰 연구 및 프로토콜 연구는 제외하였다. 초록, 학회 발표 자료, 학술지 논문을 포함하였다. 동아시아의학(Traditional East Asian medicine) 분야의 연구를 포함하였으며 인도, 페르시아 등 동아시아 지역 이외의 전통의학에 대해서는 배제하였다. 심박변이도 검사의 목적이 진단에 활용하고자 함이 아닌 치료 효과를 평가하기 위함인 문헌은 배제하였다.
초록 스크리닝과 전문 스크리닝은 한 명의 전문가에 의해 시간을 두고 중복 수행되었다. 두 결과 사이의 불일치는 문헌 선정 기준에 대한 숙고를 통해 해결하였다. 다른 데이터베이스에서 중복된 논문, 영어 이외의 언어로 작성된 논문, 그리고 논문 유형, 개념, 맥락, 관심 결과에 대한 선정 기준을 충족하지 않는 연구들은 초록 스크리닝에서 먼저 제외되었다. 전문 검토에서는 연구 설계로 인해 관심 결과에 대한 선정 기준을 충족하지 않는 연구들이 제외되었다. 초록 및 전문 스크리닝 과정에서 Endnote 20(Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, USA)이 사용되었다.
3. 데이터 추출 및 분석
데이터 추출은 사전 정의된 데이터 추출 양식을 사용하여 수행되었다. 선택된 문헌들로부터 논문 유형(학회 발표 자료 또는 학술지 논문), 저자, 출판 연도, 논문 제목, 학술지 또는 학회명, 언어에 관련된 데이터를 Endnote를 이용하여 추출하였다. 연구 수행 국가, 연구 대상 및 수, 이용한 심박변이도의 특성, 수행 과제, 그리고 수행 과제에 대한 주요 연구 결과가 수집되었다.
추출된 데이터는 포함된 연구에서 사용된 심박변이도의 특성, 연구 설계의 유형, 그리고 유형에 따른 주요 연구 결과를 요약하기 위해 분석되었다.
본 론
1. 연구 대상 문헌 선정
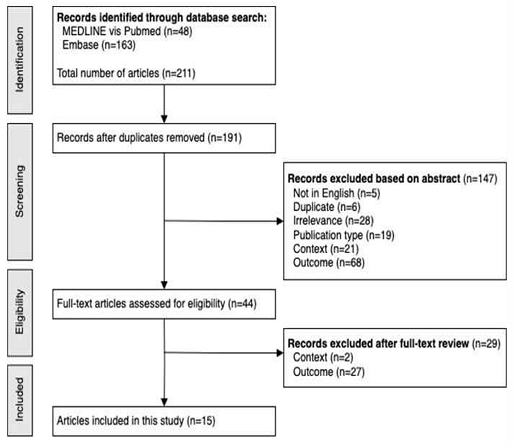
두 개의 데이터베이스에서 수행한 체계적 검색 결과, 학회 초록, 학회 발표 자료, 그리고 학술지 논문을 포함하여 총 211편의 논문이 도출되었다. 서지 관리 프로그램을 통해 20편의 중복 문헌을 제거하고 남은 191편의 논문 중에서 제목과 초록 스크리닝을 통해 147편을 제외한 후, 44편의 전문 논문에 대해 적격성 평가를 실시하였다. 초록 스크리닝에서 제외된 문헌의 경우, 언어 관련 5편, 중복 문헌 6편, 문헌의 종류 관련 19편(프로토콜 연구이거나 리뷰 연구 등), 컨셉 측면에서 관련이 없는 문헌 28편(HRV가 동음이의어로 포함된 경우 등), 한의학 및 전통 동아시아의학과 관련이 없는 문헌 21편, 결과 측면에서 진단 목적으로 연구가 설계되지 않은 경우 68편(주로 치료 수단의 효과를 평가하기 위한 목적으로 심박변이도가 사용된 경우 등)이 해당하였다. 44편의 전문 논문에 대한 적격성 평가 과정에서는 연구 목적이 진단과 무관한 경우 27편, 한의학 컨셉에 해당하지 않는 경우 2편 등 제외 기준에 해당하는 29편의 연구를 제외한 후, 최종적으로 15편의 연구가 본 연구에 포함되었다(Fig. 1).
포함된 연구들의 세부 사항은 Table 2에 제시되어 있다. 저자와 연도, 연구를 수행한 국가, 표본 대상 및 크기, 이용된 심박변이도 특징, 수행한 과제, 심박변이도에 기반한 진단과 관련된 주요 연구 결과가 나타나 있다. 2000년대에 수행된 연구가 1건, 2010년대에 11건, 2020년대에 3건의 연구가 있었다. 국가별로는 한국에서 수행된 연구가 4건, 중국 4건, 대만 5건, 일본 1건, 멕시코 1건으로 나타났다.
2. 이용된 심박변이도의 특징
심박변이도 분석은 시간 영역과 주파수 영역의 다양한 측정 방법을 사용하여 수행되었다(Table 3). 주파수 영역에서 저주파(LF)와 고주파(HF) 파워가 가장 많이 사용되어 각각 15개 연구에서 나타났으며, LF/HF 비율이 13개 연구에서 그 뒤를 이었다. 이들은 각각 교감 및 부교감 신경 활동, 부교감 신경 활동, 그리고 자율신경계 균형에 대한 정보를 반영한다. 초저주파(VLF)와 총 파워(TP)도 각각 8개 연구에서 사용되어 장기 조절 메커니즘과 전반적인 자율신경 활동에 대한 정보를 제공했다.
시간 영역 측정에서는 SDNN이 4개 연구, 평균 심박수(MHR)가 4개 연구, RMSSD가 3개 연구에서 사용되어 전반적인 심박변이도와 단기 변동성을 평가하는 데 활용되었다. SDANN은 2개 연구에서 사용되어 장기 심박변이도 구성요소를 분석했다. 이러한 측정은 전반적인 심박변이도(SDNN)와 심박변이도의 단기 구성요소(RMSSD)에 대한 보완적인 정보를 제공한다.
덜 빈번하게 사용된 측정으로는 정규화된 LF(nLF)와 HF(nHF), NN50이 각각 1개 연구에서 나타났다. 비선형 분석 방법인 근사 엔트로피(ApEn)도 1개 연구에서 사용되어 심박 동역학의 복잡성을 평가했다. 이러한 다양한 심박변이도 특징들은 다양한 생리적 및 병리적 상태에서 자율신경 기능에 대한 포괄적인 평가를 가능하게 한다.
3. 연구 설계 유형
검토된 연구들은 그 목적과 접근 방식에 따라 5개의 주요 범주로 분류되었다(Table 4). 가장 많은 연구(7건)가 수행된 범주는 'TEAM Pattern and Symptom Analysis'로, 전통 동아시아 의학(Traditional East Asian medicine; TEAM)의 패턴, 체질, 증상과 심박변이도 간의 관계를 조사하는 데 중점을 두었다. 이 중 6건(#1, #4, #6, #9, #10, #11)은 변증과 관련된 연구였으며, 1건(#3)은 증상 분석에 초점을 맞추었다. 두 번째로 흔한 범주는 'Comparative Analysis'로, 4건의 연구가 이에 해당했다. 이 연구들은 특정 조건이 있는 그룹과 없는 그룹, 또는 서로 다른 TEAM 증후군 간의 심박변이도 파라미터를 비교했다. 이 중 3건(#2, #12, #13)은 변증 관련 연구였고, 1건(#14)은 증상 관련 연구였다. 'Diagnostic Tool Development' 범주에는 2건(#5, #7)의 연구가 포함되었다. 이 연구들은 심박변이도를 사용하여 진단 설문지나 도구를 개발하거나 검증하는 데 초점을 맞추었다. 'HRV Pattern Development for Specific Conditions'와 'Physiological Indicator Correlation Analysis' 범주에는 각각 1건의 연구가 포함되었다. 전자(#8)는 특정 조건(예를 들어, 불면증 등)에 대한 허, 실, 음, 양 변증을 위한 심박변이도 패턴을 개발하는 데 중점을 두었고, 후자(#15)는 심박변이도와 다른 생리학적 지표 간의 상관관계를 분석했다. 이러한 다양한 연구 접근법은 전통적인 의학 시스템과 현대 의학을 연결하는 데 있어 다양한 심박변이도 기반 연구 설계가 가능함을 시사한다.
4. 심박변이도 기반 진단 관련 의미 있는 결과
검토 대상 문헌들에서 도출된 의미있는 결과들을 체질, 증상, 변증과 심박변이도의 유의한 관계, 그리고 질환에 대한 심박변이도 패턴 기반 새로운 변증 제시 측면에서 정리할 수 있다.
먼저, 동아시아 전통의학의 체질과 심박변이도 지표 사이에 유의미한 관계가 관찰되었다. 태양(Taiyang) 성격 점수가 높을수록 저주파(LF)와 고주파(HF) 성분이 모두 감소하여, 교감신경과 부교감신경 활동이 전반적으로 저하되는 경향을 보였다(#1112)). 한랭 체질 그룹은 열 체질 그룹에 비해 정규화된 저주파 성분(LF%)과 저주파/고주파 비율의 자연로그값(ln(LF/HF))이 낮은 경향을 나타냈으나, 통계적으로 유의미한 차이는 아니었다(#913)). 사상체질 중 소음(So-Eum) 체질 그룹은 비소음 그룹에 비해 정규화된 저주파(nLF)와 LF/HF 비율이 유의하게 낮고, 정규화된 고주파(nHF)가 높아 자율신경계의 불균형 상태를 시사했다(#1314)). 또한, VedaPulse 기술을 이용하여 분석한 중국의 9가지 기본 체질 유형 중에서는 풍(Wind) 체질 유형이 초저주파(VLF) 범위에서, 화(Fire) 체질 유형이 저주파(LF) 범위에서, 담(Phlegm) 체질 유형이 고주파(HF) 범위에서 각각 우세한 요인을 보이는 것으로 나타났다(#1015)). 이러한 결과들은 동아시아 전통의학의 체질 분류와 자율신경계 활동 사이에 밀접한 연관성이 있음을 시사하며, 체질에 따라 자율신경계의 조절 패턴이 다를 수 있음을 보여준다.
다음으로, 동아시아 전통의학에서 정의된 다양한 증상과 심박변이도 지표 간에 유의미한 관계가 관찰되었다. 흉협고만(Kyokyo-kuman)의 중증도는 LF/HF 비율과 유의한 양의 상관관계를 보여, 이 패턴이 심해질수록 교감신경 활동이 증가하는 경향이 있음을 시사했다(#316)). 반면, 심하계(心下悸; Palpitations below the heart) 증상을 보이는 그룹에서는 주간에 RMSSD와 pNN50이 높고 LF/HF 비율이 낮아, 부교감신경 활성이 증가하는 양상을 나타냈다(#1417)). 이는 심하계 증상이 자율신경계의 불균형, 특히 부교감신경의 과활성과 관련될 수 있음을 제시한다. 제2형 당뇨병 환자 중 청설(bluish tongue)이 있는 경우, 전반적으로 높은 심박변이도, 높은 LF, 높은 VLF, 낮은 TP를 보였다(#418)). 또한 화병(Hwa-Byung)의 경우, 관련 성격 특성과 증상이 심박변이도의 전반적인 감소와 부분적으로 연관되어 있음이 확인되었다(#719)). 이는 화병이 자율신경계 기능의 저하와 관련될 수 있음을 시사한다. 이러한 결과들은 동아시아 전통의학에서 정의된 증상들이 실제로 측정 가능한 생리학적 변화, 특히 자율신경계 기능의 변화와 연관되어 있음을 보여주며, 심박변이도 분석이 이러한 증상의 객관적 평가와 이해에 유용할 수 있음을 제시한다.
다양한 변증 진단과 심박변이도 지표 간에 복잡한 관계가 관찰되었다. 간기울체(Liver Qi Stagnation)의 심각도와 LF/HF 비율 사이에는 유의한 관계가 없었으나, 노르에피네프린(NE)이 LF/HF 비율과 경계적으로 유의한 연관성을 보였다. 또한, 시상하부-뇌하수체-부신(HPA) 축 경로가 지지되어, 코티솔이 ACTH와, ACTH가 간기울체의 심각도와 유의한 양의 상관관계를 나타냈다(#1520)). 혈어(Blood Stasis) 그룹에서는 SDNN, TP, LF, HF가 유의하게 낮아 전반적인 자율신경 활동의 감소를 시사했으며(#521)), 비기허증(SQDS) 환자들은 높은 LF/HF 비율과 낮은 HF를 보여 교감-부교감 불균형을 나타냈다(#1222)). 음허증(YDS) 점수가 높을수록 심박수 증가와 함께 SDANN, TP, VLF, LF, HF의 감소를 보여 자율신경계 활동의 전반적인 감소와 연관되었다(#123), #224)). 또한, 담음(Phlegm), 한증(Cold), 음허(Yin Deficiency) 변증 점수가 증가할수록 일부 부인과 질환군에서 교감 및 부교감 활동이 감소하는 경향을 보였다(#625)). 이러한 결과들은 변증 진단과 자율신경계 기능 사이에 복잡하고 다양한 관계가 존재함을 시사한다. 특히, 대부분의 변증에서 자율신경계 활동의 변화나 불균형이 관찰되었으며, 이는 변증이 실제로 측정 가능한 생리학적 변화와 연관되어 있음을 보여준다. 이러한 발견은 동아시아 전통의학 진단의 객관화와 현대 의학과의 통합에 중요한 기초를 제공할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
마지막으로 변증 개념을 활용하여 특정 질환의 심박변이도 패턴을 개발하였다. 허실음양(虛實陰陽) 개념을 기반으로 한 출산 전후 및 폐경기 불면증의 심박변이도 패턴 개발에 관한 연구가 진행되었다. 이 연구는 심박변이도 지표를 사용하여 질환을 객관적으로 허증과 실증 패턴으로 분류하였으며, 그 결과 허양(虛陽), 허음(虛陰), 실양(實陽), 실음(實陰)의 네 가지 패턴이 도출되었다(#8). 이러한 결과들은 동아시아 전통의학의 체질, 증상, 변증 개념들과 현대 의학의 자율신경계 기능 평가 사이에 의미 있는 연관성이 있음을 시사한다. 이는 동아시아 전통의학 기반의 진단 및 치료 접근법 개발에 객관적인 근거를 제공할 수 있으며, 향후 통합의학적 연구의 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
고 찰
본 연구는 주제범위 연구 방식을 채택하여 심박변이도를 활용한 한의학 및 동아시아 전통의학 진단 관련 연구의 현황을 체계적으로 고찰하였다. 주제범위 연구는 특정 연구 분야의 핵심 개념, 주요 근거 자료, 연구 동향 등을 개괄하기 위한 탐색적 문헌고찰 방법이다10). 체계적 문헌고찰과 달리 연구 질문을 보다 포괄적으로 설정하고, 연구 선정 기준을 유연하게 적용하여 관련 연구를 폭넓게 검토한다는 특징이 있으며, 이를 통해 해당 분야의 연구 범위와 특성, 지식 격차 등을 파악하고 향후 연구 방향을 제시하는 데 목적이 있다. 본 연구에서는 심박변이도와 한의학적 진단의 연계 가능성을 다각도로 조명하고, 관련 연구의 현 주소와 과제를 짚어보았으며 고찰 결과, 심박변이도가 한의학적 진단의 객관화와 현대화에 기여할 수 있는 잠재력을 가지고 있음을 확인하였다.
본 연구에서 분석한 문헌들의 연구설계 방식은 크게 다섯 가지로 분류되었다. 첫번째, TEAM Pattern and Symptom Analysis는 한의학적 변증, 체질, 증상과 심박변이도 지표 간의 상관관계를 분석하는 방식으로, 가장 많은 연구에서 채택되었다. 두번째, Comparative Analysis는 특정 질환 또는 증후군을 가진 그룹과 대조군 간의 심박변이도 차이를 비교하는 방식이다. 세번째, Diagnostic Tool Development는 심박변이도를 활용한 한의학적 진단 도구를 개발하고 검증하는 연구이다. 네번째로, HRV Pattern Development for Specific Conditions는 특정 질환에 대한 심박변이도 패턴을 개발하는 연구이다. 마지막으로, Physiological Indicator Correlation Analysis는 심박변이도와 다른 생리학적 지표 간의 상관관계를 분석하는 연구이다. 이러한 다양한 접근 방식은 심박변이도와 한의학적 개념 간의 관계를 다각도로 탐색하는 데 기여하고 있다.
특히 네번째 분류는 전통적인 이론을 현대적 생리학적 지표와 연결시키는 중요한 시도로 볼 수 있다. 본 연구에서 살펴본 #8 문헌에서 주목할 만한 점은 심박변이도를 기반으로 개발된 패턴들이 전통적인 중의학 개념과 일치하면서도 현대 수면 의학의 원리로 설명될 수 있다는 것이다. 이는 동양 의학의 전통적 진단 방법과 현대 의학의 객관적 측정 도구 간의 연결 가능성을 보여주는 중요한 발견이다. 이러한 연구 결과는 출산 전후 및 폐경기 불면증에 대한 보다 정확하고 개인화된 진단과 치료 접근법 개발에 기여할 수 있다. 심박변이도 패턴을 통해 각 환자의 불면증 유형을 객관적으로 분류하고, 이에 따른 맞춤형 치료 전략을 수립할 수 있는 가능성이 열린 것이다. 또한, 이러한 접근 방식은 동양 의학과 서양 의학의 통합적 연구 및 임상 적용에 대한 새로운 모델을 제시하고 있다. 즉, 심박변이도 분석이 한의학의 변증 이론을 객관화하고 검증하는 데 유용한 도구가 될 수 있음을 보여줌으로써 한의학의 진단 체계를 현대화하고 과학적 근거를 강화하는 데 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
본 주제범위 문헌고찰을 통해 심박변이도 연구에서 첫번째 TEAM Pattern and Syndrome Analysis와 두번째 Comparative Analysis 연구가 주요한 접근 방식으로 활용되고 있음을 확인하였다. 이 두 카테고리는 서로 구별되는 특징을 가지고 있으나, 동시에 상호 보완적인 역할을 한다. TEAM Pattern and Syndrome Analysis는 한의학 이론적 프레임워크를 현대 생리학적 측정 방법인 심박변이도와 연결하려는 시도로, 동아시아 전통의학의 진단 기준과 심박변이도 지표 간의 상관관계를 탐구한다. 이는 전통의학 이론의 과학적 검증과 현대의학과의 통합에 중요한 역할을 한다. 반면, Comparative Analysis 연구는 더 광범위한 의학적, 생리학적 상태에서의 자율신경계 기능 차이를 심박변이도를 통해 평가한다. 이 접근 방식은 특정 질병 상태나 생리적 조건이 자율신경계 기능에 미치는 영향을 객관적으로 측정하고 비교할 수 있게 한다.
본 연구에서 검토한 문헌들은 심박변이도와 한의학의 주요 개념인 증상, 변증, 체질 사이에 유의미한 연관성이 있음을 보여주고 있다. 이는 한의학적 진단 방법과 개념들이 실제 인체의 생리학적 변화를 반영할 수 있으며, 현대 의학적 방법론을 통해 객관적으로 검증될 수 있음을 시사한다. 심박변이도를 통한 한의학적 접근은 크게 증상, 변증, 체질의 세 가지 측면에서 이루어졌으며, 각각의 접근 방식에서 특징적인 연관성이 관찰되었다.
증상 측면에서, 심박변이도 지표는 특정 한의학적 증상과 연관성을 보였다. 예를 들어, 심하계 증상은 부교감신경 활성 증가(RMSSD와 pNN50의 증가, LF/HF 비율의 감소)와 관련이 있었으며, 청설을 보인 제2형 당뇨병 환자군에서는 특징적인 심박변이도 패턴(높은 심박변이도, LF, VLF, 낮은 TP)이 관찰되었다. 이러한 결과는 심박변이도 분석이 한의학적 증상을 객관적으로 평가하고 정량화하는 데 활용될 수 있음을 시사한다.
변증 측면에서는 각 변증 유형별로 특징적인 심박변이도 변화 양상이 관찰되었다. 간기울체에서는 LF/HF 비율과 노르에피네프린 사이의 연관성이 시사되었으며, 음허증에서는 전반적인 자율신경 활동의 감소가, 비기허증에서는 교감-부교감 불균형이 나타났다. 특히 주목할 만한 점은, 음허증을 대상으로 한 복수의 연구(#1, #2)에서 일관된 결과가 관찰되었다는 것이다. 두 연구 모두 음허증의 심각도가 증가할수록 전반적인 자율신경계 활동이 감소하는 경향을 보였으며, 특히 교감신경 활동(LF power)과 부교감신경 활동(HF power) 모두 감소하는 것으로 나타났다. 이는 음허증이 단순히 증상의 집합이 아니라 실제 생리적 변화와 연관된 증후군일 수 있음을 시사한다. 이러한 결과들은 변증이 자율신경계의 다양한 불균형 상태를 반영할 수 있으며, 심박변이도가 변증 진단을 객관화하는 데 기여할 수 있음을 의미한다.
체질 측면에서, 체질에 따른 심박변이도 차이는 개인의 선천적 특성이 자율신경계 기능과 밀접하게 연관되어 있음을 나타낸다. 예를 들어, 태양인에서는 전반적인 자율신경 활동의 저하가, 소음인에서는 LF/HF와 nLF의 감소, nHF의 증가로 특징지어지는 자율신경 불균형이 관찰되었다. 또한 중국의 9가지 체질 중 풍, 화, 담 체질이 각각 VLF, LF, HF 영역에서 우세한 활동을 보였다. 이는 심박변이도 분석이 체질 진단에 객관적이고 유용한 정보를 제공할 수 있음을 의미한다.
종합적으로, 본 연구에서 살펴본 문헌들은 한의학의 증상, 변증, 체질 개념과 심박변이도 지표 사이에 유의미한 연관성이 있음을 보여주고 있다. 이는 심박변이도 분석이 한의학적 진단과 평가를 객관화하고 정량화하는 데 기여할 수 있음을 시사한다. 심박변이도 분석을 통해 증상을 수치화하고, 변증별 자율신경계 특성을 규명하며, 체질 진단을 표준화할 수 있는 가능성이 제시되었다.
한편, 본 문헌 고찰 연구에는 몇 가지 한계점이 있다. 첫째, 본 고찰에 포함된 연구들의 질적 평가가 수행되지 않아, 개별 연구 결과의 신뢰성과 타당성을 객관적으로 판단하기 어렵다. 둘째, 발표 편향(publication bias)의 가능성을 배제할 수 없어, 심박변이도와 한의학적 개념 간의 관계에 대한 전체적인 연구 동향을 완전히 반영하지 못했을 수 있다. 셋째, 본 고찰의 범위가 특정 데이터베이스와 언어로 제한되어 있어, 관련된 모든 연구를 포괄하지 못했을 가능성이 있다. 넷째, 주제범위 문헌고찰의 특성상 개별 연구 결과의 통계적 종합이나 메타분석을 수행하지 않아, 효과 크기나 관계의 강도를 정량적으로 평가하지 못했다. 다섯째, 본 연구에서 문헌 선정 및 데이터 추출 과정이 한 명의 연구자에 의해 수행되고 중복 검토되었다는 점에서, 다수의 독립적인 연구자가 참여하는 체계적 문헌 고찰에 비해 선택 편향의 위험이 있을 수 있다. 이는 연구의 객관성과 재현성을 제한할 수 있는 요소로 작용할 수 있다. 마지막으로, 대부분의 연구들이 기존 진단 체계를 통해 질환, 변증, 체질을 분류한 후 각 군에서의 심박변이도 특성을 관찰하는 방식으로 이루어졌다는 점이다. 이는 심박변이도와 한의학적 진단 간의 연관성을 탐색하는 데는 의미가 있지만, 심박변이도 자체를 진단의 기준으로 삼기에는 한계가 있다. 현재까지의 연구 결과를 통해 심박변이도와 한의학적 진단 간의 유의미한 상관관계는 확인할 수 있지만, 이것이 곧바로 심박변이도의 진단적 활용으로 이어지기는 어려운 단계이다.
그러나 본 연구가 주제범위 문헌고찰 연구라는 점에서 이러한 한계점들은 일정 부분 용인될 수 있다. 주제범위 문헌고찰의 주요 목적은 특정 연구 분야의 전반적인 특성과 범위를 파악하는 것으로, 본 연구는 심박변이도와 한의학 및 동아시아 전통의학 진단 간의 관계에 대한 연구 동향을 포괄적으로 제시하는 데 성공했다고 볼 수 있다.
본 연구의 한계점에도 불구하고, 심박변이도와 한의학적 진단 간의 유의미한 연관성이 확인되었다는 점은 주목할 만하다. 이는 심박변이도의 한의학적 진단 도구로서의 잠재적 가치를 시사한다. 다만 현재 단계에서는 이러한 연관성이 곧바로 심박변이도의 독립적인 진단 지표로의 활용으로 이어지기는 어렵다. 심박변이도가 한의학적 진단에서 유효한 도구로 자리잡기 위해서는 몇 가지 과제가 남아있다. 첫째, 특정 질환, 변증, 체질에 특이적이면서도 재현성 높은 심박변이도 패턴의 규명이 필요하다. 이를 위해 대규모 전향적 연구를 통한 각 진단 범주별 심박변이도 프로파일 정립과 그 진단적 가치 평가가 수행되어야 할 것이다. 둘째, 관찰된 연관성의 임상적 의의와 기전에 대한 심층적인 연구가 요구된다.
심박변이도의 활용 방안에 대해서도 새로운 시각이 필요하다. 심박변이도를 단독 지표로 사용하기보다는 기존의 변증, 체질 진단 등과 통합적으로 활용할 때 더욱 강력한 진단 도구로 기능할 수 있을 것이다. 한의사의 전문적 판단과 심박변이도라는 객관적 지표를 종합함으로써, 보다 정밀한 진단과 치료 방향 결정이 가능해질 것으로 전망된다.
한국에서는 '수양명경락기능검사'라는 명칭으로 심박변이도 검사가 건강보험 급여 항목에 포함되어 있어, 한의학적 진단 체계와 현대 의학적 검사 방법의 통합적 접근이 가능하다. 본 연구를 기반으로 다양한 변증 및 증상, 질환에 대한 더 많은 연구가 수행되어 근거가 축적되고, 이를 바탕으로 더 많은 임상 데이터가 축적되는 선순환이 이루어진다면, 이를 통해 한의사들은 환자의 자율신경계 상태를 객관적으로 평가하고, 이를 한의학적 진단 및 치료 계획 수립에 활용할 수 있을 것이다. 대규모의 표준화된 연구를 통해 심박변이도 분석의 한의학적 활용에 대한 과학적 근거를 확립하고, 나아가 현대 한의학과 현대 의학의 융합적 발전을 도모할 수 있기를 기대한다. 이러한 노력은 한의학적 진단의 객관성과 정확성을 높이는 데 기여하고, 궁극적으로는 환자 치료의 질적 향상으로 이어질 수 있을 것이다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 2023년도 정부(교육부)의 재원으로 한국연구재단의 지원을 받아 수행된 기초연구사업임(RS-2023-00248152).
References
- Lee YS, Kim SH, Lee SW. Researches Trend of Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine in Sasang Constitution Field-from 2007 to 2010. Korean Journal of Oriental Medicine. 2012;18(1):59-74.
- Kim SH, Kim JU, Jeon YJ, Kim KH, Kim JY. Method for determining the deficient and solid pulse with a new pulse wave parameter. Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine. 2010;24(1):42-7.
-
Rundo F, Conoci S, Ortis A, Battiato S. An advanced bio-inspired photoplethysmography (PPG) and ECG pattern recognition system for medical assessment. Sensors. 2018;18(2):405.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020405]

-
Alturki FA, AlSharabi K, Abdurraqeeb AM, Aljalal M. EEG signal analysis for diagnosing neurological disorders using discrete wavelet transform and intelligent techniques. Sensors. 2020;20(9):2505.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092505]

-
Tannemaat M, Kefalas M, Geraedts V, Remijn-Nelissen L, Verschuuren A, Koch M, et al. Distinguishing normal, neuropathic and myopathic EMG with an automated machine learning approach. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2023;146:49-54.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2022.11.019]

-
Stauss HM. Heart rate variability. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2003;285(5):R927-R31.
[https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00452.2003]

- Park JJ, Lee MS, Kong KH, Go HY. Relationship between Heart Rate Variability and Cold-Heat Patternizationin Patient with Chronic Constipation. The Journal of Korean Oriental Internal Medicine. 2012;33(2).
- Lee SH, Kim JH, Roh YL, Rhee HK, Jeong SY, Jung SK, Jung HJ. Correlation between Oriental Medicine Diagnosis and the Autonomic Nervous SystemFunctions of Hyperhidrosis Patients. The Journal of Korean Oriental Internal Medicine. 2008;29(2).
- Kim SH. Review on Current Status of Use and Measurement Condition of Heart Rate Variability in Clinical Study of Korean Medicine. Journal of Acupuncture Research. 2012; 29(5): 127-137
-
Peters MD, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI evidence synthesis. 2020;18(10):2119-26.
[https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00167]

-
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Annals of internal medicine. 2018;169(7):467-73.
[https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850]

-
Zhang J, Wang T, Du J, Yuan R, Fan Y, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Han R, Zhao L. Correlations between five-pattern personality scores from traditional Chinese medicine and autonomic nervous response indicators in healthy female college students. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences. 2019;6(2):131-7.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcms.2019.03.003]

-
Wu HK, Ko YS, Lin YS, Wu HT, Tsai TH, Chang HH. The correlation between pulse diagnosis and constitution identification in traditional Chinese medicine. Complement Ther Med. 2017;30:107-12.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2016.12.005]

-
Oh HS, S. Koh, BH. Hwang, M. Heart rate variability in middle-aged adults: Use of Sasang typology to distinguish individuals susceptible to stress. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(44):e17764.
[https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000017764]

- Sorokin O. Heart rate variability-next step in the development of pulse analysis in traditional medicine and naturopathy. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17.
- Ueda YY, S. Arashima, Y. Shimabukuro, H. Relationship between autonomic nervous activity and the Kampo abdominal pattern of Kyokyo-kuman. International Medical Journal. 2012;19(4):314-6.
-
Song CC, K. Wu, Z. Liu, W. Chen, L. Zhu, W. Correlation between Palpitations below the Heart in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Autonomic Nerve Function Based on Heart Rate Variability: A Case-Control Study. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2021;2021.
[https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1945488]

-
Lo LH, P. Evaluation of blood stasis on tongue diagnosis associated with diabetes mellitus. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012;12.
[https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-12-S1-P149]

-
Chung SY, Park YB, Kim YJ, Park JW. Validation of the Hwa-Byung Scale and its relationship with cardiovascular autonomic function. European Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2015;7(4):409-16.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2015.05.003]

-
Ye J, Yu Y, Chung, RCK. Lian X. Wang X, Cheung WM, Tsang, HWH. The relationship between liver function and neurophysiological factors in depressed individuals: a cross-sectional study using an integrated “East meets West” medicine approach. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2023;14.
[https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1159785]

-
Park YJ, Yang DH, Lee JM, Park, YB. Development of a valid and reliable blood stasis questionnaire and its relationship to heart rate variability. Complement Ther Med. 2013;21(6):633-40.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2013.08.019]

-
Agnese OT. Rubén F, Lei L, Rosa ELG, Emma LE, Ismael JE, Salvador QG. Changes in Heart Rate Variability in Patients with Spleen-Qi Deficiency Syndrome. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2019;12(4):111-21.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jams.2019.07.002]

-
Lin SC, Huang ML, Liu SJ, HuangYF. Severity of Yin deficiency syndrome and autonomic nervous system function in cancer patients. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2009;15(1):87-91.
[https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0328]

-
Lin SC, Chen MF. Increased yin-deficient symptoms and aggravated autonomic nervous system function in patients with metastatic cancer. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2010;16(10):1059-63.
[https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2009.0487]

-
Park YJ, Lee JM, Park YB. Relationships between oriental medical pattern diagnosis and cardiovascular autonomic function. European Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2013;5(6):506-13.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2013.07.007]

-
Kung YY, Yang CCH, Chiu JH, Kuo TBJ. The application of yin-yang concept on heart rate variability patterns in menopausal women with insomnia. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2016:1-7.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2590-2]

- Lee EJ, Lee JH, Kho BH. Suggestion for Insurance Guarantee Reinforcement in Sasang Constitutional Examination and Counselling. Journal of Sasang constitutional medicine. 2017;29(4):299-310.