Aspergillus oryzae protease 유도 호흡기 염증모델에서 해표이진탕(解表二陳湯)의 항염증 효과
Ⓒ The Society of Pathology in Korean Medicine, The Physiological Society of Korean Medicine
Abstract
Haepyoijin-tang and its main components have been used for phlegm, cough and dyspnea. Using a respiratory inflammation model, we intend to reveal the anti-inflammatory effect and pharmacological mechanism of Haepyoijin-tang. We induced the respiratory inflammation model by Aspergillus oryzae protease and ovalbumin administration. Female Balb/c mice (8 weeks old) were classified into four groups as follows: saline control group, aspergillus oryzae protease and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation group (vehicle), inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang (200 mg/kg) administration group, inflammation with dexamethasone (5 mg/kg) administration group (n=7). To identify the anti-inflammatory effects of Haepyoijin-tang water extracts, we measured the inflammatory cell number in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and total live lung cell number. In addition, we checked eosinophil ratio and number in BALF. And Interleukin (IL)-5 level was also measured in lung cell culture supernatant. To confirm the mechanism of anti-inflammatory effects, we analyzed the activated helper T cell (CD4+CD25+ cell) and Th2 cell (CD4+GATA3+ cell) ratio and number in lung by using flow cytometry. Finally, we attempted to confirm the immune mechanism by measuring the ratio and number of regulatory T cells (CD4+Foxp3+ cell). Haepyoijin-tang extracts treatment diminished inflammatory cell, especially, eosinophil number in BALF and total live lung cell number. Moreover, IL-5 level was reduced in Haepyoijin-tang treated group. Surprisingly, Haepyoijin-tang extracts administration not only decreased the activated helper T cell but also Th2 cell population in lung. Additionally, regulatory T cell population was increased in Haepyoijin-tang administration group. Our findings proved that Haepyoijin-tang extract have anti-inflammatory efficacy by suppressing Th2 cell activation and promoting regulatory T cell population.
Keywords:
Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae, Eosinophil, Type 2 helper T cell, Regulatory T cell서 론
천식은 기도의 과민성(airway hyper-responsiveness), 점액 과분비 및 호산구를 비롯한 염증세포 침윤등 복합적인 염증작용에 의해 유발되는 질환이다1). 천식은 유전적인 소인이 있는 개인이 외부 알레르겐(allergen)과 같은 환경적 요인에 노출되었을 때 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있다2). 지난 20동안 천식의 유병률은 급격하게 증가하였으며, 그 이유는 위생의 개선과 대기 오염에 의한 것으로 생각된다3). 즉, 선진국 질환으로 알려진 알레르기 천식의 경우 청소년기에 알레르기 비염 및 아토피 피부염과 함께 높은 빈도로 발생한다4). 천식의 면역학적 병리기전을 살펴보면, 만성적인 기도염증, 2형 보조 T 세포(Th2 cell)의 활성 및 Interleukin (IL)-5와 같은 사이토카인의 분비 증가이다. 특히 IL-5는 호산구의 생존과 활성을 증가시키며, 결과적으로 세포 독성을 유발하여 천식 악화에 기여한다5).
알레르기성 천식을 유발하는 알레르겐은 실내와 실외 기원으로 구분할 수 있다. 실내 알레르겐은 통년성 알레르겐으로 정의되며 진균류(fungus), 고양이등 동물의 비듬(dander), 바퀴벌레(cockroach) 및 집 먼지 진드기(house dust mite)가 대표적이다. 실외 알레르겐은 계절성 알레르겐으로 정의되며 꽃가루(pollen)가 대표적이다6,7). Aspergillus oryzae (누룩곰팡이)와 같은 진균류 유래 알레르겐의 호흡기 염증유도 메커니즘 연구는 많이 진행되었는데, 주된 내용은 다음과 같다. 1) 혈관 및 림프관의 투과성을 증가시키고 2) 보체 단백질을 활성화하며 3) 기도 상피세포의 염증유도 cytokine의 생성을 유발한다6,7). 천식을 유발하는 진균류는 11종 이상 알려져 있으며 Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus fumigatus, Penicillium citrinum, Cladosporium herbarum 및 Alternaria alternate등이 대표적이다.
천식 유발 동물모델은 많이 개발되어 있는데, 가장 대표적인 방법은 chicken egg ovalbumin (OVA)을 항원으로, aluminum sulfate (Alum)를 adjuvant로 혼합하여 감작(sensitization)하고, 호흡기에 OVA를 투여하는 것이다8). 상기 모델은 실제 환자의 천식 유발 병리기전과는 차이가 있어, 최근에는 좀 더 질병의 발생 과정과 유사한 진균류 알레르겐을 이용하여 천식을 유도하는 방법이 점차 활용되고 있다9).
해표이진탕은 『古今醫鑑』에서 처음 기재된 처방으로 哮喘證을 치료하는 것으로 알려져 있다. 哮喘證은 風寒에 의해 痰飮이 유발되어 喘이 유발되는 證으로서 현대의 알레르기 천식과 유사한 것으로 설명할 수 있다. 기존의 해표이진탕 선행 실험 연구결과를 살펴보면 폐 손상 회복 효과10), Guinea Pig의 기관지 평활근 이완에 미치는 효과11) 및 OVA를 이용한 기관지 염증의 완화 효과12)가 대표적이다. 그러나 실제 천식 환자의 유발 환경과 유사한 진균류 유도 천식 모델에서 해표이진탕의 효과를 살펴본 연구결과는 부족하다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 Aspergillus oryzae protease를 이용하여 천식을 유도한 모델에서 해표이진탕의 염증 완화효과를 확인하고 그 메커니즘을 규명하고자 한다.
연구대상 및 방법
1. 처방 재료 및 추출과정
해표이진탕의 구성 본초인 반하(半夏), 진피(陳皮), 적복령(赤茯苓), 자소엽(紫蘇葉), 마황(麻黃), 행인(杏仁), 상백피(桑白皮), 자완(紫菀), 천패모(川貝母), 길경(桔梗) 및 생강(生薑) 11종은 모두 Omniherb에서 구입하였다. 11종 본초를 혼합하여 전기추출기(COSMOS-660; Kyungseo E&P, 인천, 대한민국)를 사용하여 98 kPa 압력에서 2시간 동안 100 °C 증류수에서 추출하였다. 추출 후 표준여과망 (no.270, 53 μm, Chung Gye Sang Gong Sa, 서울, 대한민국)을 이용하여 여과하고 동결 건조하여 분말을 제조하였다. 얻어진 동결건조 분말의 수율은 21.37 %이다. 각 본초의 원산지, 구입처 및 혼합 비율은 별도로 Table 1에 기재하였다.
2. 동물실험
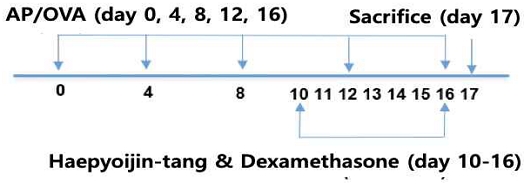
Balb/c 마우스 암컷 8주령을 대한바이오링크(충청북도, 대한민국)에서 구입하였다. 모든 실험쥐에게 살균수와 음식이 공급되었으며, 병원균이 없는 상황에서 사육되었다. 실험 목적에 따라서 각 그룹별 7마리씩 4개 그룹으로 구분하였다. 생리식염수 투여군(Saline control; SC), 누룩곰팡이 단백분해효소(Aspergillus oryzae protease; AP / Sigma P6110)와 난황단백(Ovalbumin; OVA / Sigma A5503) 혼합 투여 호흡기 염증 유도군(A), 호흡기 염증 유도 및 해표이진탕 투여군(Haepyoijin-tang), 호흡기 염증 유도 및 덱사메타손(Dexamethasone / Sigma D1756) 투여군(Dex)으로 구분하였다. 염증 유도를 위해 AP 5 μg과 OVA 25 μg을 4일 간격으로 5번 (Day 0, 4, 8, 12, 16) 비강 내(intra-nasal) 투여하였다(Fig. 1). 해표이진탕과 Dexamethasone은 마지막 7일 동안 7번 경구 내(intra-oral)로 각 200 mg/kg과 5 mg/kg이 투여되었다(Fig. 1). 모든 실험 과정 및 동물 사육은 상지대학교 동물실험윤리위원회의 승인을 받아 수행되었으며, 규정을 준수하여 실험을 진행하였다(승인번호 2019-12).
기관지 폐포 세척액(BALF)의 획득은 최종 염증 유도 및 약물 투여 후 18시간 뒤 수행되었다. BALF를 얻기 위해 20 게이지 카테터(Jelco, St. Paul, 미네소타, 미국)를 사용하여 기관에 삽입하였다. 그 후 PBS (한림제약, 서울, 대한민국) 1.0 ml를 주입하여 세척한 후, 약 0.8 ml를 획득하였다. BALF 내 세포는 HEMA3 용액(Fisher HealthCare, 피츠버그, 미국)을 이용하여 고정하였다. 그 후 cytospin (Shadon Cytospin4, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, 메사추세츠, 미국)을 이용하여 원심 분리하였다. 고정 된 세포는 상온에서 건조 후 라이트 김자(Wright-Giemsa) 방법을 이용하여 염색하였다. 그 후 도립 형 위상차 현미경(Zeiss, 오버코헨, 독일)을 이용하여 세포를 관찰하였다. 각 마우스 개체별로 총 세포수를 분석하였으며, 각 세포는 호산구, 호중구, 대식세포 및 림프구로 분류하였다. 총 세포 수에 각 세포의 비율을 곱하여 각 세포 수를 도출하였다. 분석은 연구자가 각 실험 군에 대해 블라인드 처리된 상태에서 진행되었다.
폐 조직에서 단일 세포(single cell suspension)를 획득하기 위해 기존 연구방법을 이용하였다13). 간략히 설명하면, 폐 조직을 Lung dissociation kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch-Gladbach, Germany)를 사용하여 연화한 후 gentleMACSTM Dissociator (Miltenyi Biotec)를 이용하여 분해하였다. 폐 조직 생존 단일세포의 수(total live lung cell)는 TC20 automated cell counter (Biorad, 캘리포니아, 미국)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 유세포 분석은 이전 연구에서 수행한 방법으로 진행하였다14). 유세포 분석을 위해 다음과 같은 형광 항체를 이용하여 염색하였다. Fluorescence isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-CD4 (GK1.5), phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-GATA3 (16E10A23), Allophycocyanin (APC)-cy7 conjugated anti-CD25 (PC61), Alexa 647 conjugated anti-Foxp3 (MF-14) (Biolegend, 캘리포니아, 미국)를 이용하여 세포에 항체를 부착하였다. LSRFortessa X-20 (BD Bioscience, 캘리포니아, 미국)을 이용하여 데이터를 획득하였고, FlowJo 소프트웨어(Treestar, 오리건, 미국)를 이용하여 데이터 분석을 진행하였다.
IL-5 분석은 폐 조직을 단일세포로 분획한 후 96시간 동안 배양하여 그 상층 액을 획득 한 후 ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) 기법을 이용하여 측정 하였다. 간략하게 설명하자면, 0.2 x 106의 세포를 24 well plate에 배양하면서 자극 없이 배양한 조건(Spontaneous)과 anti-CD3와 anti-CD28 항체(BD Bioscience)를 이용하여 자극한 조건(re-stimulation)으로 구분하여 96시간 후 그 상층액을 TRFK5 항체와 TRFK4 항체(BD Bioscience)를 이용하여 cytokine 수준을 측정하였다.
3. 통계분석
데이터는 평균 ± SEM으로 표시하였고 생리 식염수 그룹과 AP OVA 유도 염증 그룹 간 차이, AP OVA 염증 그룹과 해표이진탕 및 Dexamethasone 그룹 간 차이는 일원배치 분산분석(one way analysis of variance; one way ANOVA) 검정을 이용하였다. 사후 검정 방법으로 던넷 검정(Dunnett’s test)을 이용하였다. P<0.05의 경우 통계적으로 유의한 것으로 간주하였다. 또한 Prism v.10 software (GraphPad Inc., 캘리포니아, 미국)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
결 과
1. 해표이진탕 투여에 의한 폐기도세척액(BALF)의 총 염증세포와 폐 세포 수 감소
대조군에 비해 AP OVA로 유도된 염증 그룹에서 BALF의 총 염증세포 수가 통계적으로 유의하게 증가한 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 2a). 또한, 양성 대조군인 dexamethasone을 투여한 경우 선행 연구결과와 같이 BALF 내 총 염증세포 수가 통계적으로 유의한 수준으로 감소한 것을 확인하였다15)(Fig. 2a). 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 AP OVA로 증가된 BALF 내 총 염증세포 수가 감소한 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 2a). 대조군 대비 AP OVA로 유도된 쥐에서 폐 세포 수가 통계적으로 유의한 수준으로 증가하였으며, 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 dexamethasone과 유사한 수준으로 감소하였다(Fig. 2b). 본 결과를 통해 AP OVA 투여가 호흡기 염증을 효과적으로 유도하였으며, 해표이진탕 투여는 양성대조군인 dexamethasone과 유사한 수준으로 BALF 내 총 면역세포 수와 폐 세포 수를 감소시키는 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 2).
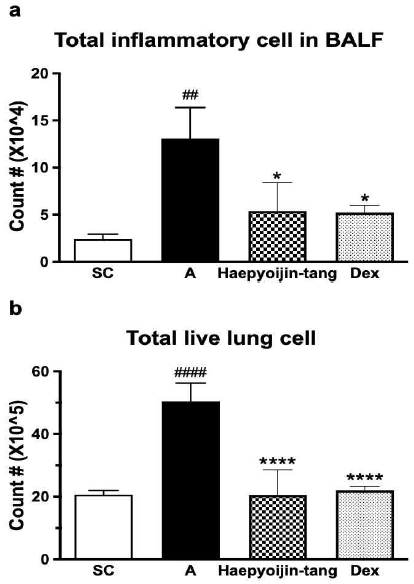
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on total inflammatory cell counts in BALF and total live lung cell counts. (a) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on total cell counts in BALF cells. (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on total live lung cell counts. SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7). ##P<0.01, ####P<0.0001 compared with the SC group, *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001 compared with the A group.
2. 해표이진탕 투여에 의한 폐기도세척액(BALF)의 호산구(eosinophil) 감소
알레르기 반응에서 핵심적인 염증유도 선천 세포인 호산구를 분석한 결과 대조군 대비 AP OVA 투여에 의해 그 비율과 수가 통계적으로 유의하게 증가한 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3). 양성 대조군인 dexamethasone을 투여한 경우 호산구의 비율과 수가 크게 감소한 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3). 해표이진탕을 투여한 경우 호산구의 비율과 수가 역시 통계적으로 유의한 수준으로 감소한 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3). 본 결과는 Fig. 2에서 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 총 염증 세포 및 폐 세포가 감소한 결과를 구체적으로 분석한 것으로, 해표이진탕이 알레르기 특이적인 항염증 효과가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
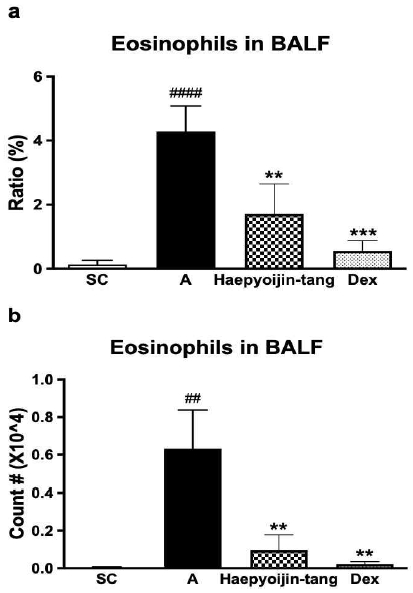
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on eosinophil counts in BALF. (a) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on proportion of eosinophils in BALF cells. (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on counts (number) of eosinophils in BALF cells. SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7). ##P<0.01, ####P<0.0001 compared with the SC group, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with the A group.
3. 해표이진탕 투여에 의한 폐 조직 내 Interleukin (IL)-5 생산 감소
호산구의 활성 및 생존에 중요한 cytokine으로 알려진 IL-5 수준을 두 조건에서 확인하였다. 첫 번째는, 폐 세포를 96시간 동안 그대로 배양한 것으로(spontaneous culture) 마우스를 부검한 당시 폐 조직의 cytokine 생산 현황을 살펴보기 위한 것이다. 두 번째는, 폐 세포를 anti-CD3/28 항체로 자극한 상태에서 96시간 동안 배양한 것으로(re-stimulation), 항체가 helper T cell을 자극하여 활성을 유도하므로, 부검한 당시 helper T cell 중 type2 helper T cell (Th2)로의 분화 및 활성 정도를 확인하기 위한 것 이다. 특정 자극 없이 배양한 조건에서, 대조군에서는 IL-5가 거의 검출되지 않았다(Fig. 4a). AP OVA 염증 유도군의 폐 조직에서는 IL-5가 매우 증가한 경향성을 보였다(Fig. 4a). Dexamethasone 투여 군에서는 염증 유도 군에 비해 cytokine이 감소한 결과를 확인하지 못하였고, 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 감소한 경향을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 4a). Anti-CD3/28 항체 자극 조건에서는 대조군에서도 IL-5가 유의한 수준으로 검출되었으나, 대조군 대비 AP OVA 염증 유도 군에서는 IL-5가 매우 증가한 경향성을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 4b). Dexamethasone 및 해표이진탕 투여 군에서는 염증 유도 군에 비해 cytokine 수준이 매우 감소한 경향을 확인하였다(Fig. 4b). 이 실험은 helper T cell의 활성정도를 확인하는 것이 목적 이므로, 그 결과는 다음과 같이 해석 할 수 있다. AP OVA 유도군의 폐 세포를 항체로 자극한 경우 매우 양의 IL-5가 검출된 것은 부검당시 상태가 AP OVA 염증 유도에 의해 Th2 세포가 많이 존재하며 활성화 되어 있는 것으로 이해할 수 있다. AP OVA 염증 유도 군에서 항체 자극 없이 배양한 조건에서 IL-5가 검출된 것도 부검 당시 Th2 세포로 많이 분화되어 활성화 되어 있다는 것을 나타낸다. 또한, 해표이진탕 및 dexamethasone 투여에 의해 IL-5가 감소한 경향성이 있는 것은, 약물 투여에 의해 부검당시 Th2 세포의 비율 및 수가 실험 군에 비해 감소한 것으로 설명할 수 있다.
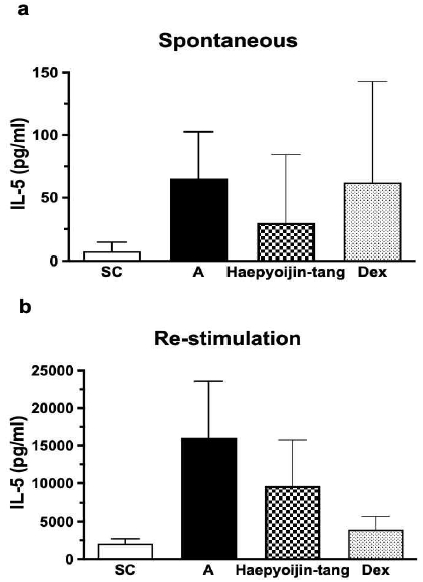
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on IL-5 in lung. (a) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on IL-5 in lung (spontaneous culture). (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on IL-5 in lung (antibody re-stimulation). SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7).
4. 해표이진탕 투여에 의한 폐 조직 내 활성 보조 T 세포(CD4+CD25+ cell) 및 2형 보조 T 세포(CD4+GATA3+ cell) 비율 및 수 감소
Fig. 4의 결과를 바탕으로 활성 보조 T세포의 비율과 수를 분석하기 위해 유세포 분석(flowcytometry analysis)을 진행하였다. CD25는 IL-2 receptor의 alpha chain으로 발현이 높을수록 보조 T세포가 활성화 된 것으로 해석할 수 있다16). 대조군 대비 AP OVA 염증 유도 군에서 활성 보조 T 세포의 비율과 수가 통계적으로 유의하게 증가한 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 5). 또한, dexamethasone 투여에 의해 T 세포의 활성이 감소한 것을 확인하였으며, 선행 연구결과와 일치한다17). 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 통계적으로 유의한 수준으로 활성 보조 T 세포의 비율과 수가 감소한 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 5). 이 결과는 Figure 4에서 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 항체자극 조건에서 IL-5 수준이 감소한 이유를 더 구체적으로 설명해 주는 결과로, 부검당시 활성 보조 T세포의 비율이 감소한 것을 유세포 분석 기법을 통해 확인한 것이다.
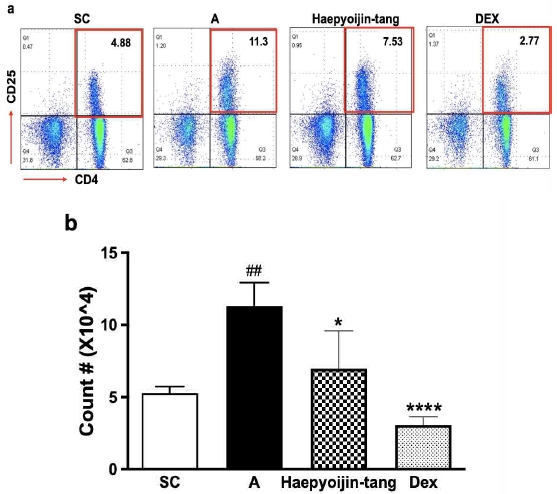
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on activated helper T cell in lung. (a) Representative plots of a single individual from each group. The number inside the plots indicate the frequency of CD4+CD25+ cells. (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on counts of activated helper T cell in lung. SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7). ##P<0.01 compared with the SC group, *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001 compared with the A group.
Fig. 4와 5의 결과를 종합적으로 분석해보면, 해표이진탕 투여는 IL-5를 생산하는 보조 T 세포의 활성도, 비율 및 수를 감소시키며, ELISA와 유세포 분석 기법을 통해 확인할 수 있었다. 활성 보조 T 세포 중 IL-5를 생산하는 것으로 알려진 2형 보조 T 세포(Th2)18)의 비율과 수를 폐 조직에서 확인하기 위해 유세포 분석 기법을 통해 GATA3가 발현되어 있는 보조 T 세포를 분석하였다. 흥미롭게도, Fig. 4b 및 Fig. 5의 결과와 일치하게 대조군 대비 AP OVA 염증 유도군에서 Th2 세포의 비율과 수가 증가하고 dexamethasone 및 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 감소하는 경향을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 6).
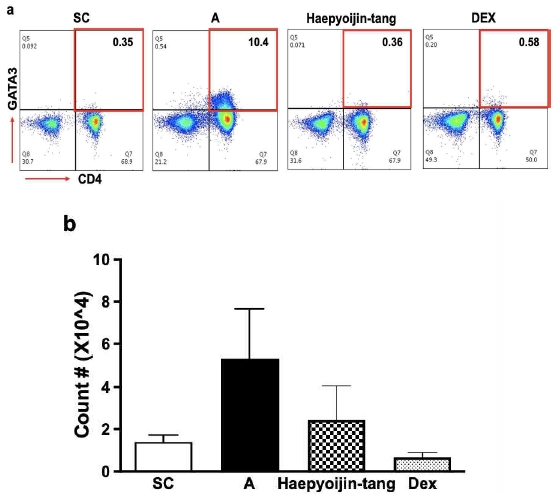
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on type 2 helper T cell in lung. (a) Representative plots of a single individual from each group. The number inside the plots indicate the frequency of CD4+GATA3+ cells. (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on counts of type 2 helper T cell in lung. SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7).
4. 해표이진탕 투여에 의한 폐 조직 내 조절 T 세포 (CD4+Foxp3+ cell)의 비율 및 수 증가
Fig. 4에서 6까지 결과를 종합해보면, 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 과민 염증반응의 핵심 염증세포인 호산구가 감소한 것은 해표이진탕이 Th2 세포의 활성 및 수 감소를 유도하여 결국 IL-5의 생산 및 분비가 감소 한 것을 이유로 해석 할 수 있다. 나아가 Th2 세포의 활성 및 수 감소의 세포면역학적 면역기전을 추가로 확인하고자, 염증반응을 억제하고 항상성을 유지하는 것으로 알려진 조절 T 세포19)의 비율과 수를 확인 하였다. 대조군 대비 AP OVA 염증 유도 군에서는, 기존에 알려진 바와 같이 염증상황을 종결하기 위한 반응으로 조절 T 세포의 비율 및 수가 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있었다20). 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 조절 T 세포의 비율과 수가 더욱 증가한 경향을 확인할 수 있었으며, dexamethasone 투여에 의해서는 조절 T 세포의 비율과 수가 증가하지 않은 것을 확인하였다. Dexamethasone이 steroid 계열의 약물로서 전반적인 염증 반응을 억제하여 조절 T세포의 증가를 유도하지 않는다는 것은 기존의 연구결과와 일치한다21).
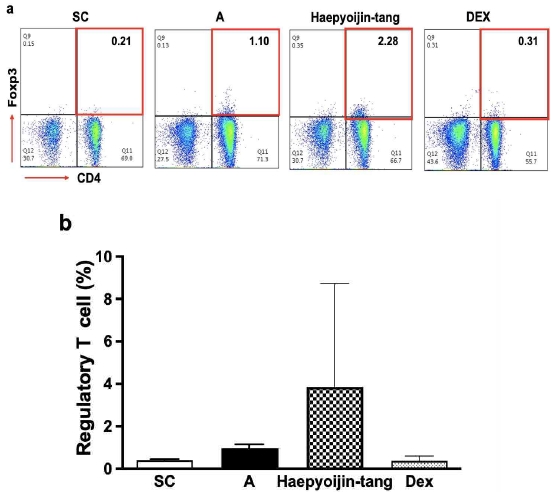
Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on regulatory T cell in lung. (a) Representative plots of a single individual from each group. The number inside the plots indicate the frequency of CD4+Foxp3+ cells. (b) Effect of Haepyoijin-tang on counts of regulatory T cell in lung. SC, saline control group; A, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with vehicle group; Haepyoijin-tang, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with Haepyoijin-tang group; DEX, Aspergillus oryzae and ovalbumin induced respiratory inflammation with dexamethasone group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7).
고 찰
천식의 유병률은 지속적으로 증가하고 있으며, 특히 COVID-19와 같은 감염성 호흡기 질환이 발생할 경우, 천식을 기저질환으로 겪고 있는 환자의 사망률이 급격하게 증가하는 등 기저 호흡기 질환은 사회적으로 중요한 문제로 대두되고 있다22). 뿐만 아니라, 미세먼지와 자동차 배기가스등 환경오염 물질 역시 천식을 악화시키는 중요한 요인으로 작용한다. 호흡기 염증성 질환은 한의학에서 哮喘證 또는 肺脹證에 해당하는 것으로 風寒邪氣에 의해 발생하며 痰과 瘀血이 挾雜하게 되면 증후가 지속되며 악화 된다.
기존 천식 모델은 대부분 OVA를 aluminum sulfate와 함께 복강주입(intra-peritoneal injection)을 통해 감작한 후 추가적인 OVA의 호흡기 투여를 통해 염증을 유도 하였다. 이 모델은 OVA에 특이적인 T 세포 및 B 세포의 활성을 유도하여, 강력한 알레르기 염증반응을 유도할 수 있기에 많이 활용되었다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 실제 환자는 이러한 인위적 감작 없이 알레르겐의 호흡기 노출을 통해 알레르기 천식이 유발되는 점을 고려해보면, 생리적으로 적절하지 않는 모델이라 할 수 있다. 따라서, 호흡기 직접 감작을 통한 염증 유도 모델이 적합하며, 본 연구에서는 처음으로 Aspergillus oryzae protease를 이용하여 해표이진탕의 호흡기 항염증 효과를 규명 하고자 하였다. 특히, 기존의 선행연구결과에서 전통적인 OVA 감작 모델을 이용하여 해표이진탕의 항염증 효과를 규명 하였기에, 본 모델에서 항염증 효과를 재확인하고, 추가적인 메커니즘을 규명하고자 하였다.
해표이진탕 투여는 호흡기 염증을 뚜렷하게 완화하는 결과를 나타내었다. BALF 내 총 염증세포 수의 감소 및 폐 조직 세포 수의 감소를 유도하였을 뿐 아니라, 알레르기 천식에서 가장 핵심적인 세포로 알려진 호산구23)의 비율 및 수가 감소한 결과를 확인할 수 있었다. 호산구의 활성 및 생존을 조절하는 IL-5의 수준도 폐 세포 배양을 통해 확인한 결과 해표이진탕 투여군에서 감소한 경향이 있는 것을 확인하였다. 위와 같은 결과를 통해 진균류 호흡기 감작 모델에서도 해표이진탕의 항염증 효과를 확인할 수 있었다. 추가적으로, 염증 완화 효과의 약리 기전을 살펴보고자, 알레르기 후천 면역의 대표적인 조절자(Orchestrator)인 Th2 세포의 활성과 수를 유세포 분석 기법을 활용하여 확인 하였는데, 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 그 활성 및 수가 감소한 것을 확인하였다. 또한, T 세포 및 선천세포의 염증작용을 억제하여 항상성을 유지하는 조절 T 세포의 수를 확인한 결과, 해표이진탕 투여군에서 증가하는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
본 연구를 통해 한의학에서 오랜 기간 임상적으로 哮喘證에 사용해온 해표이진탕의 항염증 효과와 그 약리기전을 임상의 질병유발 상황과 가장 유사한 진균류 이용 모델에서 확인할 수 있었다. 앞으로, 한약을 이용한 호흡기 약리기전 연구에서 본 연구 모델을 이용하여 효과를 확인한다면, 전 임상 연구결과의 의미가 더욱 확대될 수 있을 것으로 생각한다. 또한 이번 연구에서는 확인하지 못했지만, 조절 T 세포의 구체적인 억제 기전, 핵심 구성 본초 및 구체적인 세포 내 signaling을 규명하는 연구가 추가적으로 이뤄지길 기대한다.
결 론
해표이진탕은 AP OVA로 유도된 호흡기 염증 모델에서 염증반응을 완화한다. 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 폐기도세척액(BALF) 및 폐 조직에서 염증세포 수가 감소한 것으로 확인 할 수 있다. 호산구는 알레르기성 호흡기 염증반응에서 가장 핵심적인 역할을 하는 것으로 알려져 있는데, 해표이진탕 투여에 의해 BALF에서 호산구의 수와 비율이 감소하는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 또한, 호산구 생존 및 활성 조절에는 IL-5 cytokine이 핵심적인데, 항체를 이용해 보조 T세포를 활성화 한 폐 세포 배양 조건에서, 해표이진탕 투여 마우스의 경우 폐 세포의 IL-5 생산이 감소하는 경향을 확인 하였다. IL-5의 생산을 통해 호산구의 활성을 조절하는 것을 포함하여, 2형 면역 반응(type2 immunity)에서 총괄적인 조절자로 알려진 2형 보조 T 세포(CD4+GATA3+ cell)를 유세포 기법으로 분석 결과, 해표이진탕 투여가 2형 보조 T 세포의 비율과 수를 감소시키는 것을 확인하였다. 세포면역학적 메커니즘을 추가적으로 분석하기 위해, 항상성을 유지하고 염증반응을 억제하는 것으로 알려진 조절 T 세포(CD4+Foxp3+ cell)의 비율과 수를 분석하였다. 해표이진탕 투여는 dexamethasone과는 달리 조절 T 세포의 비율과 수를 증가시켜 염증반응의 억제를 유도하는 것을 확인하였다.
Acknowledgments
본 결과물은 2023년도 교육부의 재원으로 한국연구재단의 지원을 받아 수행된 지자체-대학 협력 기반 지역혁신 사업의 결과입니다.(2022RIS-005)
References
-
Beerweiler CC, Masanetz RK, Schaub B. Asthma and allergic diseases: Cross talk of immune system and environmental factors. Eur J Immunol. 2023;53(6):e2249981.
[https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.202249981]

-
Umetsu DT, Mclntire JJ, Akbari O, Macaubas C, DeKruyff RH. Asthma: an epidemic of dysregulated immunity. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(8):715-20.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0802-715]

-
Tiotiu AI, Novakova P, Nedeva D, Chong-Neto HJ, Novakova S, Steiropoulos P, et al. Impact of Air Pollution on Asthma Outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(17):6212.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176212]

-
Tsuge M, Ikeda M, Matsumoto N, Yorifuji T, Tsukahara H. Current Insights into Atopic March. Children (Basel). 2021;8(11):1067.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/children8111067]

-
Hammad H, Lambrecht B. The basic immunology of asthma. 2021;184(6):1469-85.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.016]

-
Roche N, Chinet TC, Belouchi NE, Julié C, Huchon GJ. Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and bioelectric properties of airway epithelium: role of cysteine proteases. Eur Respir J. 2020;16(2):309-15.
[https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.16b20.x]

-
Kawamoto S, Mizuguchi Y, Morimoto K, Aki T, Shigeta S, Yasueda H, et al. Cloning and expression of Der f 6, a serine protease allergen from the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1454(2):201-7.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(99)00041-1]

-
Chun JM, Lee AR, Kim HS, Lee AY, Gu GJ, Moon BC, et al. Peucedanum japonicum extract attenuates allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting Th2 cell activation and production of pro-inflammatory mediators. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;211:76-88.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.09.006]

-
Shin K, Kataru RP, Park HJ, Kwon BI, Kim TW, Hong YK, et al. TH2 cells and their cytokines regulate formation and function of lymphatic vessels. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6196.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7196]

- Park DI, Rhee HK. A study of Effects of Haepyoyijintang on the Analgesia, Anticonvulsion, Antipyresis and O₃ Poisoned Lung in rats and mice. Kyung Hee Uni Ori Med J. 1986;9:463-74.
- Park CS, Han SH. Effects of Haepyoyangjintang and Haepyoijintang Extract On the Contraction of Isolated guinea pig trachea smooth muscle. J Int Korean Med. 1990;11(2):68-79.
- Baek DJ, Jung HJ, Rhee HK, Jung SK. The Effects of Haepyoijin-tang on the Cytokines in Asthma Model. J Int Korean Med. 2020:21(3):57-67.
-
Kwon BI, Hong S, Shin K, Choi EH, Hwang JJ, Lee SH. Innate type 2 immunity is associated with eosinophilic pleural effusion in primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:577-85.
[https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201302-0295OC]

-
Kwon BI, Kim TW, Shin K, Kim YH, Yuk CM, Yuk JM, et al. Enhanced Th2 cell differentiation and function in the absence of Nox2. Allergy. 2017;72(2):252-65.
[https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12944]

-
Seo YS, Kim HS, Lee AY, Chun JM, Kim SB, Moon BC, et al. Codonopsis lanceolata attenuates allergic lung inflammation by inhibiting Th2 cell activation and augmenting mitochondrial ROS dismutase (SOD2) expression. Sci Rep. 2019;9:2312
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38782-6]

-
Lee AR, Chun JM, Lee AY, Kim HS, Gu GJ, Kwon BI. Reduced allergic lung inflammation by root extracts from two species of Peucedanum through inhibition of Th2 cell activation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;196:75-83.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.015]

-
Kim SB, Lee AY, Chun JM, Lee AR, Kim HS, Seo YS, et al. Anthriscus sylvestris root extract reduces allergic lung inflammation by regulating interferon regulatory factor 4-mediated Th2 cell activation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;232:165-75.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.12.016]

-
Lee HJ, Takemoto N, Kurata H, Kamogawa Y, Miyatake S, O’Garra A, et al. Gata-3 Induces T Helper Cell Type2 (Th2) Cytokines Expression and Chromatin Remodeling in Committed Th1 Cells. J Exp Med. 2000;192(1):105-16.
[https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.192.1.105]

-
Vignali DA, Collison LW, Workman CJ. How regulatory T cell work. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:523-32.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2343]

-
Ray A, Khare A, Krishnamoorthy N, Qi Z, Ray P. Regulatory T cells in many flavors control asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2010;3:216-29.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2010.4]

-
Sbiera S, Dexneit T, Reichardt SD, Michel KD, Brandt J, Schmull S, et al. Influence of Short-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy on Regulatory T cells In Vivo. PLoS One. 2011.
[https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024345]

-
Yang MJ, Koh HY, Moon SY, Yoo IK, Ha EK, You S, et al. Allergic disorders and susceptibility to and severity of COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;146(4):790-8.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.08.008]

-
Walford HH, Doherty TA. Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic asthma: a US perspective. J Asthma Allergy. 2014;7:53-65.
[https://doi.org/10.2147/JAA.S39119]